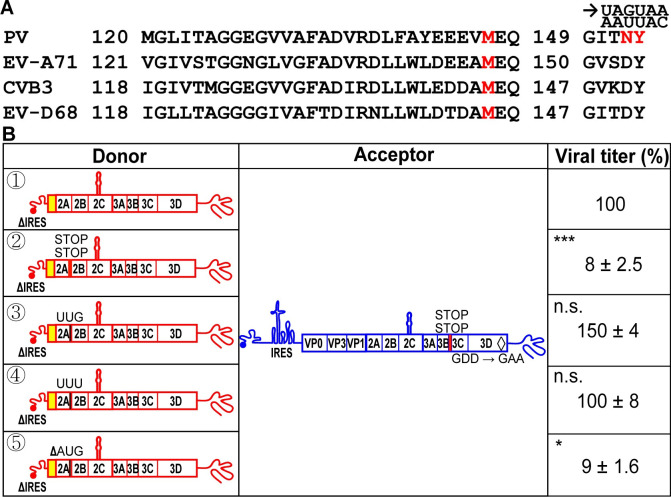
Fig 9. Deletion of a conserved AUG in the 2A-coding sequence reduces translation of the donor RNA leading to a reduction in viral RNA recombinants.
(A) Primary amino acid sequence alignment of a portion of 2A sequence from PV, EV-A71, CVB3, and EV-D68. Numbers refer to 2A protein sequence. The conserved methionine is shown in red. The sites for the insertion of two STOP codons are shown in red; the codons AAU and UAC were changed to UAG and UAA, respectively. (B) Comparison of infectious virus produced by the indicated donor RNAs with the specified modifications: ①: ΔIRES; ②: Insertion of two STOP codons after the 2A-coding sequence (2A STOP); ③: AUG to UUG; ④: AUG to UUU; ⑤: ΔAUG. Sites for the modifications are depicted. In all cases, the acceptor RNA contained two STOP codons after 3B-coding sequence (3B STOP) and the mutation that inactivates the RdRp (GDD to GAA). Indicated are the relative viral titers with the average viral titer from recombination using ΔIRES donor (①) and acceptor set as 100% (7,500 pfu/mL, mean ± SEM; n = 3). Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired, two-tailed t test (* indicates p < 0.05, *** indicates p < 0.001, n.s. indicates not significant). The 2A STOP and ΔAUG reduced viral recombinants, while the AUG to UUG and AUG to UUU did not. Numerical data provided as Supporting information (S1 Data). IRES, internal ribosome entry site; PV, poliovirus; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.