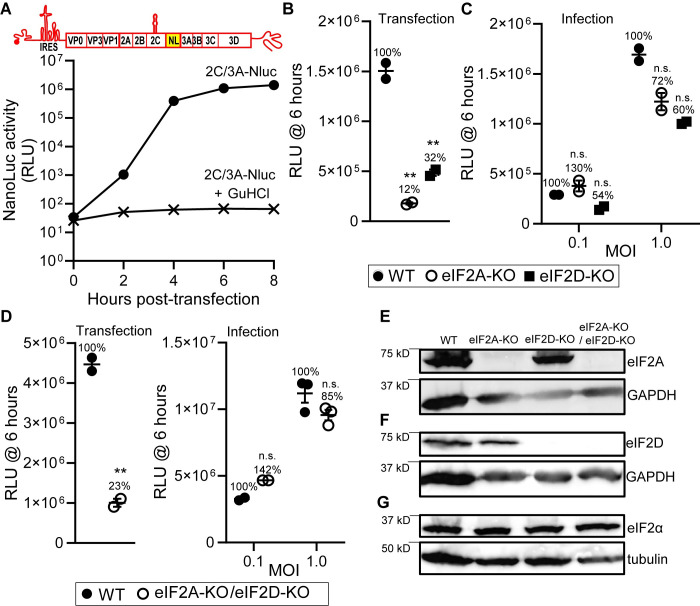
Fig 12. Contribution of eIF2A and eIF2D to translation of enteroviral RNAs.
(A) NanoLuc activity in HAP1 WT cells transfected with a full-length PV genome with the nanoLuc-coding sequence embedded between 2C- and 3A-coding regions (2C/3A-Nluc). As a control, the PV 2C/3A-Nluc RNA was transfected in the presence of GuHCl. Numerical data provided as Supporting information (S1 Data). (B) Comparison of nanoLuc activity at six hours posttransfection using PV 2C/3A-Nluc RNA in HAP1 WT, eIF2A-KO, and eIF2D-KO cells. Data from one of two biological replicates with similar results, each with two technical replicates. Numerical data provided as Supporting information (S1 Data). (C) Comparison of nanoLuc activity at six hours postinfection using an MOI of 0.1 or 1 in HAP1 WT, eIF2A-KO, and eIF2D-KO cells. Data from one of two biological replicates with similar results, each with two technical replicates. Numerical data provided as Supporting information (S1 Data). (D) Comparison of nanoLuc activity at six hours posttransfection using PV 2C/3A-Nluc RNA (Transfection), and at six hours postinfection using an MOI of 0.1 or 1 (Infection) in HAP1 WT, and eIF2A-KO/eIF2D-KO cells. Data from one of two biological replicates with similar results, each with two or three technical replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired, two-tailed t test (** indicates p < 0.01, n.s. indicates not significant). Numerical data provided as Supporting information (S1 Data). (E-G) Western blot analysis of eIF2A (panel E), eIF2D (panel F), and eIF2α (panel G) in HAP1 WT, eIF2A-KO, eIF2D-KO, and eIF2A-KO/eIF2D-KO cells. Cells were processed for western blot analysis and probed using anti-eIF2A, eIF2D, and eIF2α antibodies. GAPDH and tubulin were used as a loading control for western blot. Blots provided in Supporting information (S1 Raw Images). GuHCl, guanidine hydrochloride; KO, knockout; PV, poliovirus; RLU, relative light unit; WT, wild-type.