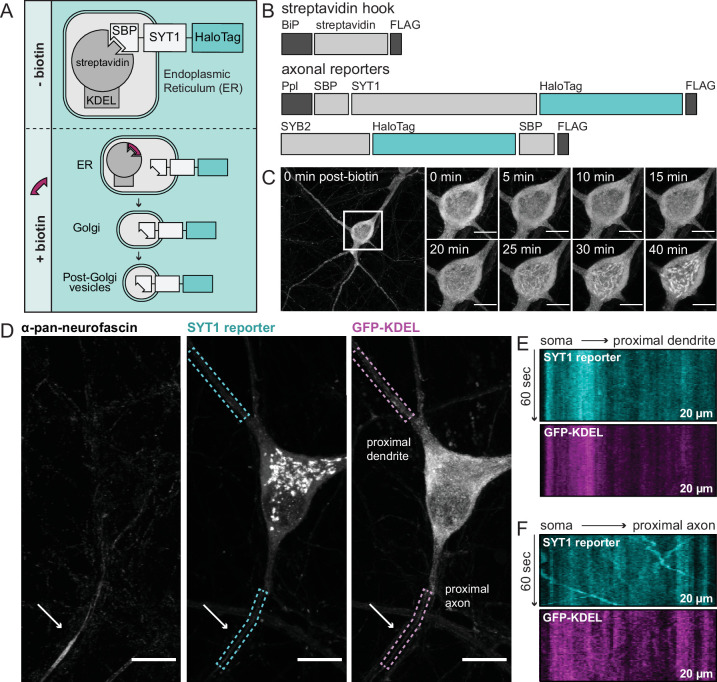
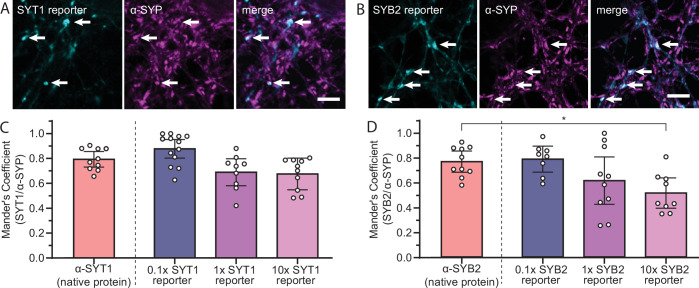
Figure 1. Using retention using selective hooks (RUSH) to study egress of synaptic vesicle (SV) proteins from the soma of cultured rat hippocampal neurons.
(A) A cartoon of RUSH; pre- and post-biotin conditions are shown. (B) Schematic of the streptavidin hook, and SYT1 and SYB2 reporter RUSH constructs: BiP, a signal peptide that drives translocation into the ER; FLAG, provides a means to detect each construct; SBP, streptavidin-binding peptide; Ppl, a pre-prolactin leader sequence to translocate the SBP into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In all cases the reporter is a HaloTag. (C) Representative super-resolution fluorescent live-cell MAX projection images from rat neurons at 15 days in vitro (DIV). Images of SYT1 reporter immediately after biotin addition with enlarged insets to detail the time course of release. Inset scale bar is 10 µm in panels (C–D). Since SYT1 and SYB2 behaved similarly, only SYT1 images are shown in panels (C–F). (D) Image of a neuron, 30 min after biotin addition, expressing the streptavidin hook, SYT1 reporter, and ER-targeted GFP (GFP-KDEL). Live-cell labeling with an anti-pan-neurofascin antibody was used to identify the axon initial segment (AIS; arrow); dendrites were identified by morphology and because they lacked an AIS. SYT1 was labeled with JF549 HaloTag ligand, and kymographs of this reporter, along with GFP-KDEL, were generated from the regions indicated by dashed boxes (20 µm long). Kymographs from a proximal dendrite (E) and proximal axon (F) are shown.
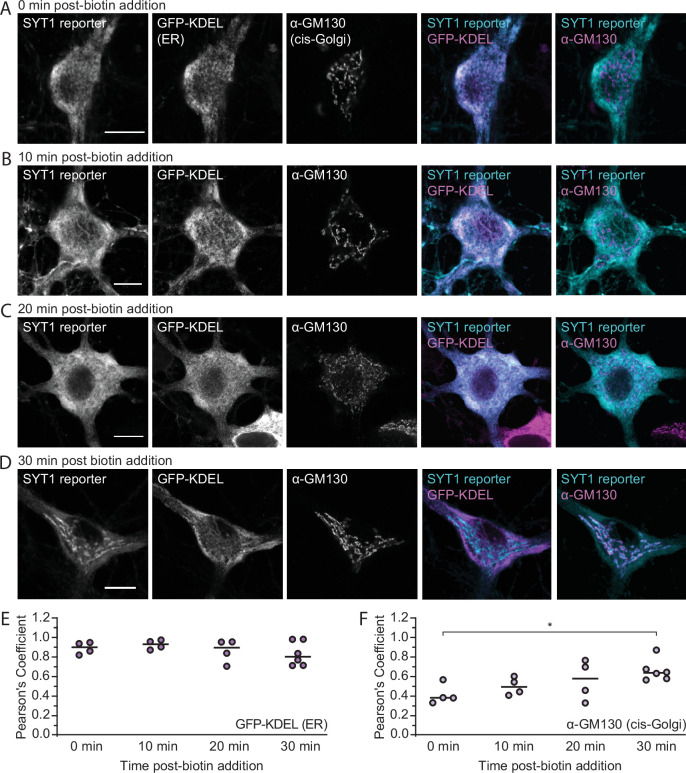
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. The SYT1 reporter localizes to the early secretory pathway after biotin addition.
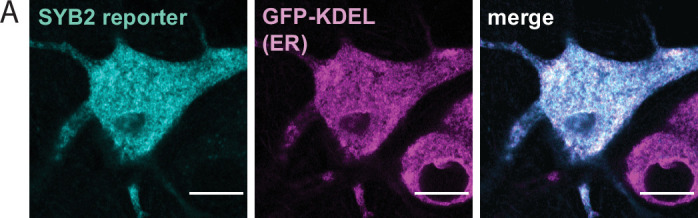
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. The SYB2 reporter is retained in the endoplasmic reticulum prior to biotin addition.