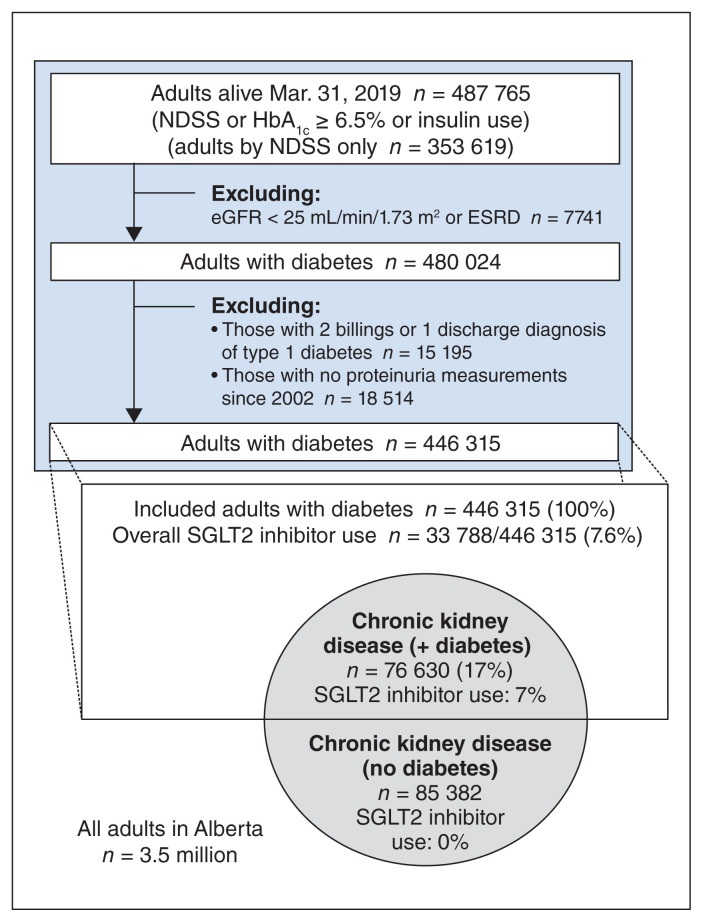
Figure 1:
Adults with diabetes and prevalence of adults with chronic kidney disease eligible for SGLT2 inhibitor treatment (per definitions in Table 1). Note: eGFR = estimated glomerular filtration rate; ESRD = end-stage renal disease; HbA1c = hemoglobin A1c; NDSS = National Diabetes Surveillance System, referring to a well-accepted administrative-database case definition for diabetes; SGLT2 = sodium–glucose cotransporter 2. Encircled areas show SGLT2 inhibitor indications, in the style of a Venn diagram, and are not drawn to scale.