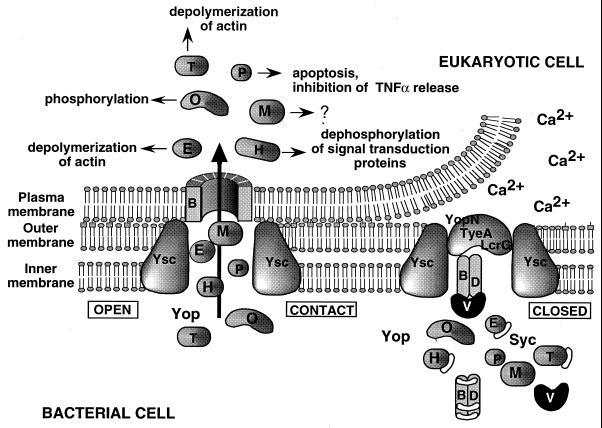
FIG. 2.
A tentative model for the interaction between Yersinia and a macrophage. When Yersinia is placed at 37°C in a rich environment, the Ysc secretion apparatus is installed and a stock of Yop proteins is synthesized. Some of these proteins are capped with their specific Syc chaperones, which presumably prevent premature associations. As long as there is no contact with a eukaryotic cell, the YopN-TyeA-LcrG plug blocks the Ysc secretion channel. Upon Ca2+ depletion or contact with the eukaryotic target cell, the secretion channel opens and the YopB translocator inserts in the eukaryotic cell with the help of YopD and LcrV. The Yop effectors (YopE, YopH, YopM, YopO/YpkA, YopP/YopJ, and YopT) are then transported through the secretion channel and translocated across the plasma membrane, guided by the translocators. YopE and YopT act on the cytoskeleton, while YopP/YopJ induces apoptosis and inhibits the release of TNF-α.