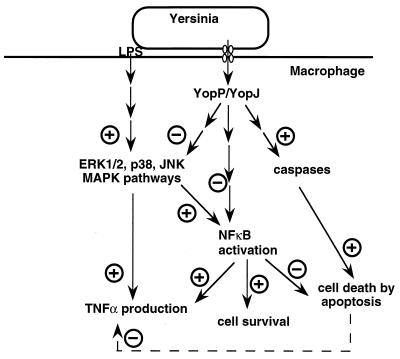
FIG. 5.
Model showing the effects of Yersinia spp. on the macrophage intracellular cascades. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activates the ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 MAPK pathways, leading to increased TNF-α production. Activated MAPKs can lead to NF-κB activation; activated NF-κB can, in turn, enhance TNF-α transcription. Translocated YopP/YopJ induces macrophage apoptosis by a mechanism involving caspase activation. It also downregulates MAPKs and impairs NF-κB activation, two effects that could explain the YopP/YopJ-induced reduction of TNF-α production. See the text for details and references.