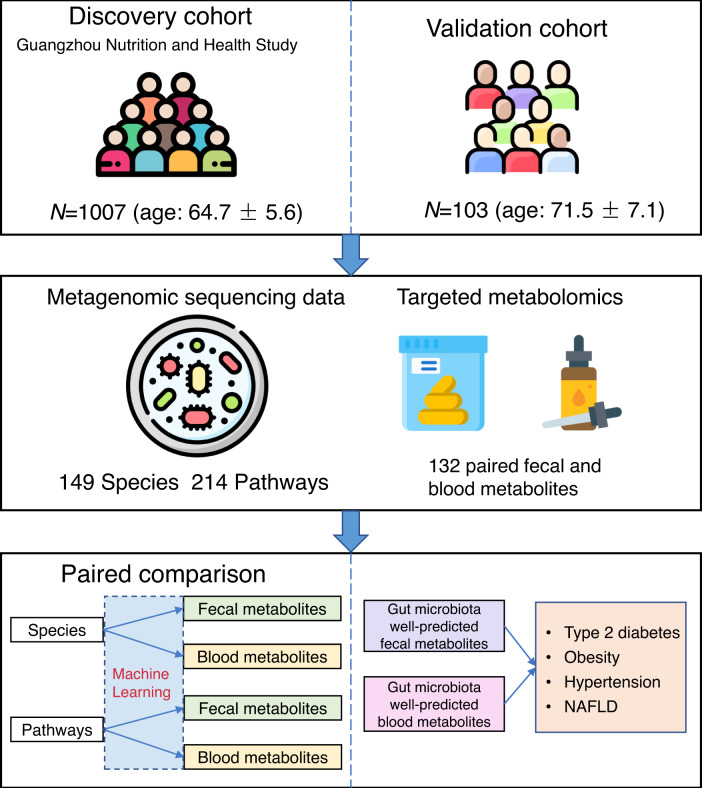
Fig. 1. Workflow of the present study.
A total of 1007 participants from the Guangzhou Nutrition and Health Study with matched gut metagenomic and fecal and blood metabolomics data and without taking antibiotics within two weeks are included in this study. Shotgun metagenomic sequencing is performed for fecal samples to obtain the metagenomic data, including taxonomic composition and microbial pathways. A targeted metabolome profiling is performed to obtain the fecal and blood metabolomics data. After removing metabolites with missing rate ≥ 0.2 or with relative standard deviation ≥ 0.3, 132 matched fecal and blood metabolites are remained for subsequent analysis. We estimate the gut microbiota-fecal/blood metabolite associations using the machine learning pipeline, and compare the associations of taxonomic composition/microbial pathways with paired fecal and blood metabolites. We then explore the associations of gut microbiota-related fecal and blood metabolites with cardiometabolic diseases. We further replicate the identified significant associations in an independent validation cohort. This figure has been designed using images from Flaticon.com. NAFLD nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.