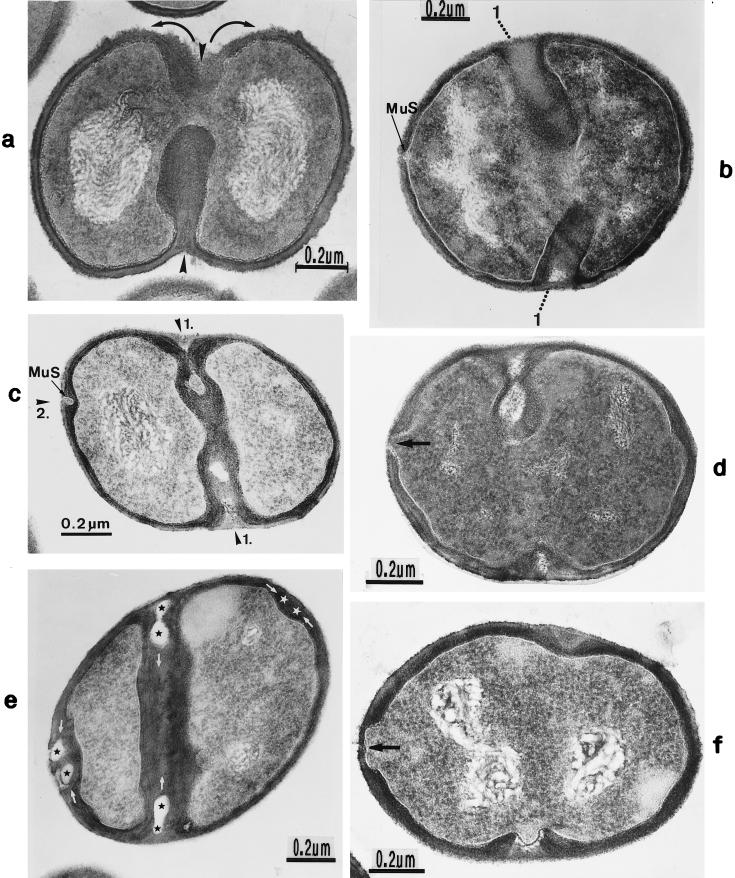
FIG. 19.
Thin sections of staphylococcal cells grown in the presence of 0.05 (a) or 0.1 (b to f) μg of penicillin/ml. (a) Huge amounts of fibrillar wall material deposited at the cross wall tips have prevented a fatal tearing apart of the nascent cross wall (arrowheads). The premature initiation of cell separation has only resulted in a limited increase of cell size (arc-shaped arrows). (b) A murosome (MuS) is deposited at the initiation site of the second division plane between the cytoplasmic membrane and the peripheral wall. 1, first division plane (reproduced with permission from reference 50). (c) A murosome (MuS) is found within the peripheral wall of the second division plane (2). 1, first division plane (reproduced with permission from reference 50). (d) By attack from the inside, one murosome has disintegrated a sector of some inner layers of the peripheral wall, the so-called secondary wall (arrow), at the initiation site of the second cell division. The outer layers of the peripheral wall, the so-called primary wall, are not yet affected. (e) A pair of murosomes (black stars at the left side) is found deposited within the peripheral wall at the initiation site of the second division plane. The white stars mark the initiation site of the second division plane of the other daughter cell (reproduced with permission from reference 48). (f) By attack from the inside, a pair of murosomes has disintegrated a sector of the secondary wall at the initiation site of the second division plane, leaving behind a rather extended gap in the inner layer of the peripheral wall (arrow) without, however, affecting its outer layers.