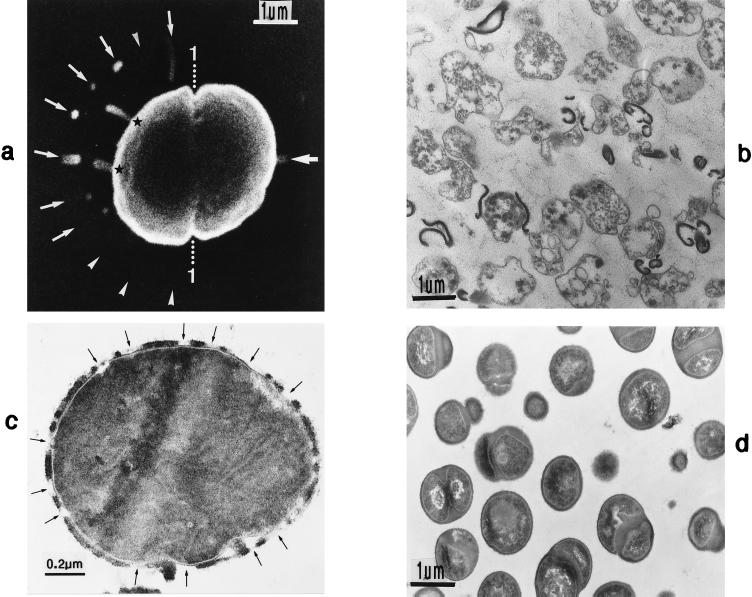
FIG. 23.
Scanning electron micrograph (a) and thin sections (b to d) of staphylococcal cells grown in the presence of penicillin. (a) By varying the osmolarity of the growth medium, several murosomes of the second division plane are ejected simultaneously (arrows); arrowheads mark supposed ejections of murosomes. 1, first division plane (reproduced with permission from reference 50). (b) After a 4-h treatment with 0.1-μg/ml penicillin most cells undergo bacteriolysis and show different degrees of cellular disintegration. (c) Simultaneous treatment with penicillin (0.1 μg/ml) and lysozyme (1 mg/ml) prevents bacteriolysis; the protoplast even remains stabilized in spite of multiple breakages in the peripheral cell wall (arrows) (reproduced with permission from reference 51). (d) After 4 h of simultaneous treatment with 0.1-μg/ml penicillin and 100-μg/ml Evans blue, the staphylococci seem to be intact, although about 99% are already dead.