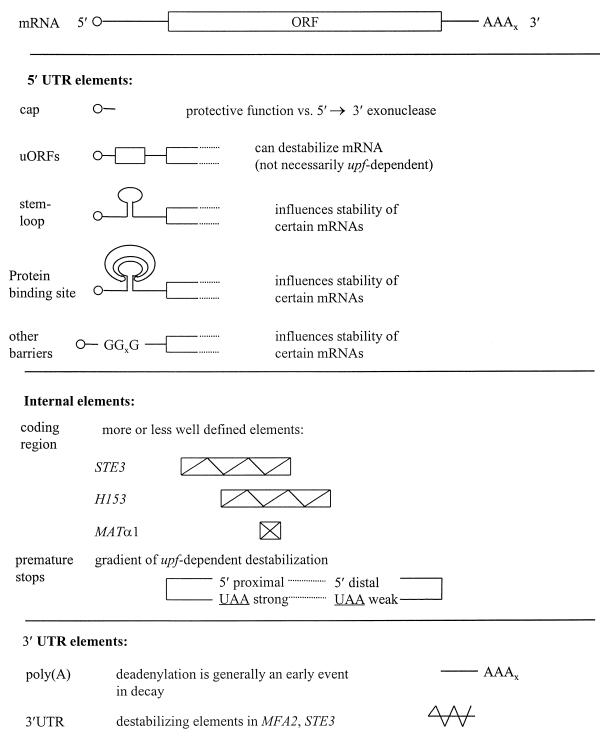
FIG. 16.
Features of yeast mRNAs influencing stability. The major types of mRNA stability determinant reported so far for S. cerevisiae are shown. The majority of these elements act to destabilize the mRNAs in which they have been studied. Internal stop codons (here indicated as UAA) can cause strong destabilization in 5′-proximal positions (strong) but have less or no effect at more distal positions (weak). Apart from the cap or poly(A) tail, it is not clear whether discrete (and transferable) stabilizing elements exist.