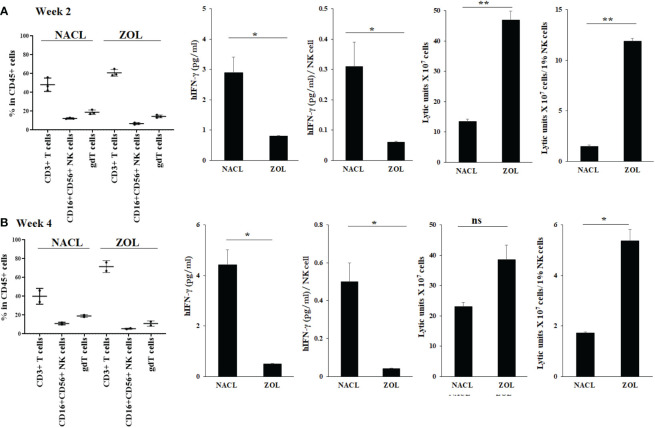
Figure 3.
Human CD45+ immune cell percentages, IFN-γ secretion and NK-cell mediated cytotoxicity in oral gingival cells of NACL or ZOL-injected and tooth extracted hu-BLT mice. Hu-BLT mice were administered with either 0.9% NACL or ZOL (500 µg/kg) via IV followed by maxillary left first molar extraction as described in Materials and Methods section. Two weeks (n=3) (A) and four weeks (n=2) (B) after injections, mice were euthanized and oral gingival tissues were harvested to obtain single cell suspension. Surface expression of CD45+CD3+, CD45+CD16+CD56+, and CD45+CD3+gdT+ in oral gingival cells were determined using flow cytometric analysis as described in the Materials and Methods. Oral gingival cells mice were cultured (2 × 106 cells/2ml) with IL-2 (1000 U/ml) for three days, after which the supernatants were harvested and the levels of IFN-γ was determined using specific ELISA. IFN-γ secretion was determined per human CD45+ cells using human CD45+ percentages obtained by flow cytometric analysis. IFN-γ per one NK cell were determined using CD16+CD56+ percentages obtained by flow cytometric analysis. Oral gingival cells were used as effector cells in standard 4-hour 51Cr release assay against human OSCSCs tumors. Lytic units (LU) 30/106 cells were determined using inverse number of effector cells required to lyse 30% of OSCSCs × 100. LU per 1% NK cells were determined using CD16+CD56+ percentages obtained by flow cytometric analysis (A, B). **(p value 0.001-0.01), *(p value 0.01-0.05) ns (no significance).