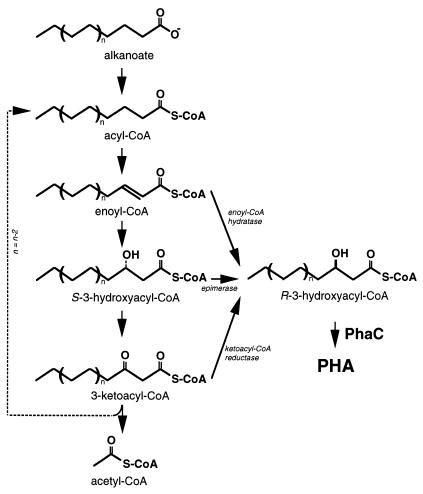
FIG. 9.
Biosynthetic pathway for msc-PHA from hydrocarbons. Fluorescent pseudomonads of rRNA homology group I can derive monomers for PHA from fatty acid degradation. Intermediates from the β-oxidation cycle can be converted to (R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA by a hydratase (H), epimerase (E), or reductase (R) activity, whose nature is currently unknown. Any or all of these three enzymes and PHA polymerase determine the limits to the substrate specificity, which is from C6 to C16 3-hydroxy fatty acids.