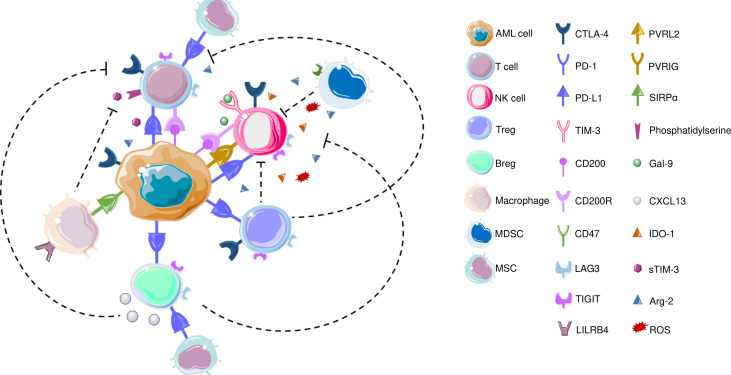
Figure 2.
CTLA-4, which is also expressed on T cells and NK cells is the first ICP that is reported to be commonly overexpressed in AML to inhibit T cell responses. In terms of T cells, increased frequency of PD-1+CD4+ T cells as well as PD-1+/CD8+ cells co-expressing TIM3 or LAG3 were reported in AML patients’ bone marrow samples. LSCs also secrete Gal-9 that leads to the elimination Th1 effector cells. LILRB4 is expressed on monocytic leukemic cells and interact with T cells to alter their function. CD200 is also expressed on AML cells that engage in CD200R on T cells and NK cells. Similar to T cells, PD-L1 expression has been detected on Bregs in AML patients. Recently, blocking PD1/PD-L1 axis along with inhibiting CXCL13 has been increased chemotherapeutic efficacy, and CXCL13 has been suggested as a novel ICP; TIGIT is also expressed on BREGs, though both these findings are yet to be confirmed in AML BM samples. TAMs express CD47 that protects phagocytosis of AML LSCs. AML: acute myeloid leukemia; Arg-2: Arginase 2; Breg: B regulatory cell; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4; CXCL-13: CXC chemokine ligand 13; Gal-9: Galectin-9; IDO-1: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; LAG3: Lymphocyte-activation gene 3; LILRB4: Leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptor B4; MDSC: myeloid-derived suppressor cell; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; NK cell: Natural killer cell; PD-1: Programmed death – 1; PD-L1: Programmed death ligand 1; PVRIG: Poliovirus receptor related immunoglobulin domain containing; PVRL2: Poliovirus receptor-related 2 (Nectin-2); ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SIRPα: Signal regulatory protein α; sTIM-3: soluble TIM-3; TIGIT: T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3; Treg: T regulatory cell; VISTA: V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation.