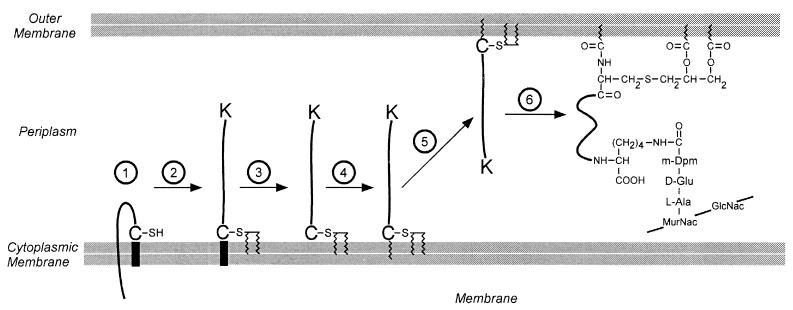
FIG. 12.
Lipid and peptidoglycan attachment of the murein (Braun’s) lipoprotein of E. coli. The complete processing of the lipoprotein occurs in several discrete steps. 1, The protein is exported from the cytosol by virtue of a type II N-terminal leader peptide. 2, The cysteine residue of the leader peptide is modified by the addition of diacylglycerol. 3, The leader peptide is removed by the type II leader peptidase. 4, The newly liberated amino terminus is acylated. 5, The protein is translocated to the periplasmic side of the outer membrane. 6, The C-terminal lysine residue of the lipoprotein is amide linked to a carboxyl group of the diaminopimelic acid at position 3 of a wall peptide. Like the surface proteins of gram-positive bacteria, the lipoprotein is amide linked to the peptidoglycan. However, in this case the cell wall donates the carboxyl group rather than the amino group to this bond.