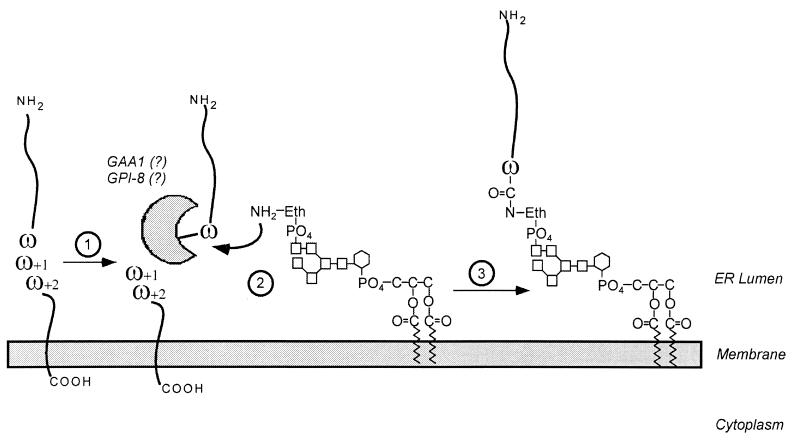
FIG. 14.
Attachment of a GPI anchor to the C-terminal end of a polypeptide chain. 1, polypeptides entering the secretory pathway are transiently anchored to the membrane of the ER via the hydrophobic portion of the C-terminal GPI-anchoring signal. 2, cleavage occurs between the ω and ω+1 residues. 3, the newly liberated carboxy-terminus of the ω residue is amide linked to the amino group of the ethanolamine of the GPI anchor. This mechanism is similar to the mechanism by which cell wall sorting of surface proteins is proposed to occur in gram-positive bacteria.