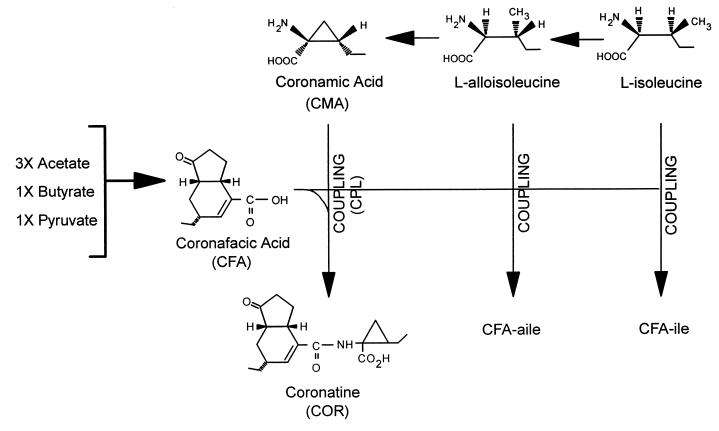
FIG. 5.
Biochemical pathways involved in the synthesis of COR and coronafacoyl compounds in P. syringae pv. glycinea PG4180. COR consists of a polyketide component, CFA, coupled (CPL) via amide-bond formation to an amino acid component, CMA. CFA is synthesized as a branched polyketide from three acetate units, one pyruvate unit, and one butyrate unit via an unknown sequence of events (196). CMA is derived from isoleucine via alloisoleucine and cyclized by an unknown mechanism (160, 195). CMA functions as an intermediate in the COR biosynthetic pathway, which indicates that cyclization of l-alloisoleucine to form CMA occurs before CFA and CMA are coupled (170). The coronafacoyl analogues, CFA-Ile and CFA-aIle result from amide bond formation between CFA and isoleucine and alloisoleucine, respectively, and are not utilized further in the synthesis of COR.