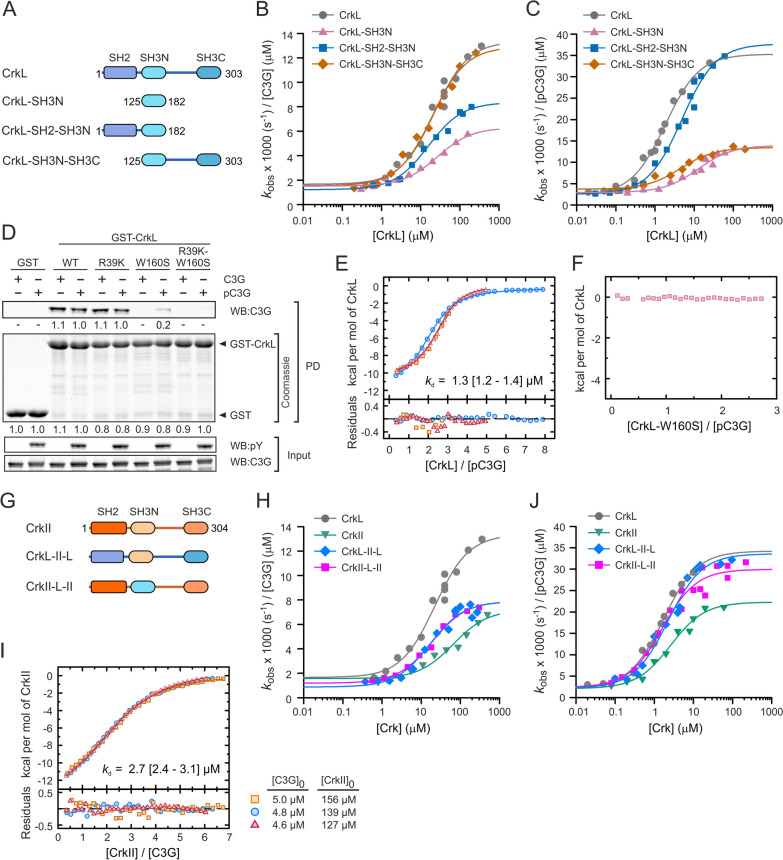
Fig. 4.
Activation of C3G by CrkL, CrkII, and their constituent domains. A Schematic representation of the domain structure of CrkL and the deletion mutants analyzed. B Analysis of the dose-dependent activation of C3G (1 µM) by CrkL full-length and the indicated fragments. Lines in (B, C, H, and J) are the fitted sigmoidal activation models. C Dose-dependent activation of Src-phosphorylated C3G (pC3G, 0.2 µM) by CrkL and its deletion mutants. D Pull-down (PD) analysis of the binding of GST-CrkL, wild type and mutants, to C3G and pC3G. C3G was detected in the PD and in the input samples by western blot (WB). Phosphorylated C3G was detected with an antibody that recognizes phospho-Tyr (pY). Numbers are the relative quantitation of the bands. E ITC isotherms of the binding of CrkL to pC3G, three independent titrations are shown. The thermogram of a representative experiment is shown in Additional file 1: Fig. S5D. F ITC analysis of the titration of pC3G with the SH3N-inactive mutant W160S of CrkL. No signal was detected. The corresponding thermogram is shown in Additional file 1: Fig. S5E. G Schematic representation of the domain structure of CrkII and the CrkL-CrkII chimeric proteins. H Dose-dependent analysis of the activation of C3G (1 µM) by CrkII and the CrkII-CrkL chimeric proteins. I ITC isotherms (three independent titrations) of the binding of CrkII to C3G. The thermogram of a representative experiment is shown in Additional file 1: Fig. S5F. J Dose-dependent analysis of the activation of pC3G (0.2 µM) by CrkII and the CrkII-CrkL chimeric proteins. Rate constants in (B, C, H, and J) are shown as the specific activities per 1 µM C3G for comparison