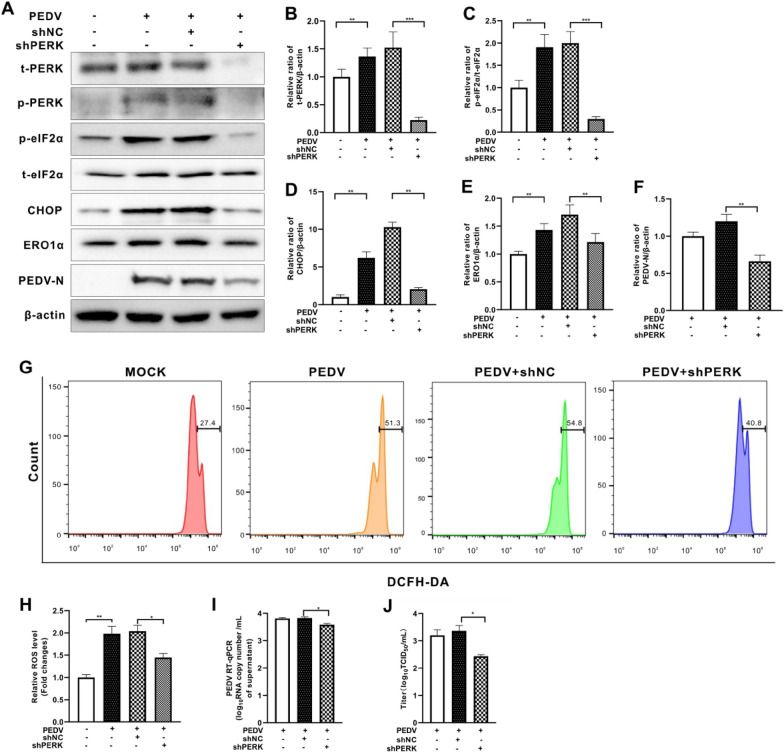
Figure 2.
Inhibition of PERK reduced cellular ROS levels and viral replication in PEDV-infected Vero E6 cells. Both the PERK-silenced (shPERK) Vero E6 cells and control cells (shNC) were infected with PEDV (MOI = 0.001) for 36 h. A The effects of perk knockdown on eIF2α, CHOP, ERO1α, and PEDV N expression were shown by Western blotting. β-actin was used as loading control. B Ratios of PERK to β-actin. C Ratios of p-eIF2α to t-eIF2α. D Ratios of CHOP to β-actin. E Ratios of ERO1α to β-actin. F Ratios of N to β-actin. G Cells collected at 36 hpi were measured for changes in cytosolic ROS level by flow cytometry after incubation with 10 μM DCFH-DA for 30 min at 37 °C. H The changes in cytosolic ROS levels were evaluated according to the mean value of DCFH-DA fluorescence intensity and expressed as fold changes between mock- and treated-cells. The effects of PERK inhibition by shRNA on viral replication, shown as viral RNA copy numbers measured by RT-qPCR (I) and virus titer (J). The bar charts in B to F, H to J represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.