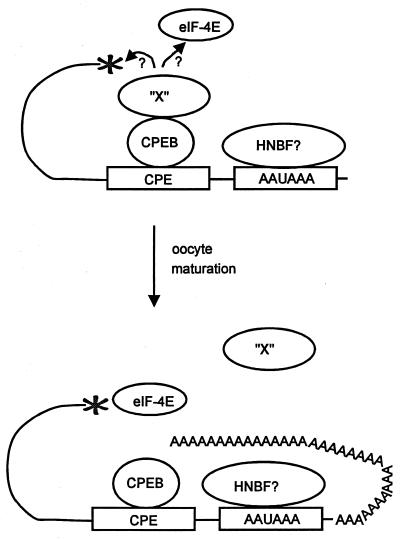
FIG. 2.
Model for CPE-mediated translational repression and activation. In immature oocytes, CPEB binds both the CPE and a hypothetical factor, factor X. Factor X, in turn, prevents translation either by interacting with the cap or by preventing eukaryotic initiation factors (i.e., eIF-4E) from recognizing the cap. A possible hexanucleotide binding factor (HNBF), which could be CPSF, is also indicated. Following oocyte maturation, CPEB induces cytoplasmic polyadenylation, which disrupts CPEB-factor X interaction and allows initiation factor binding to the cap and translation initiation.