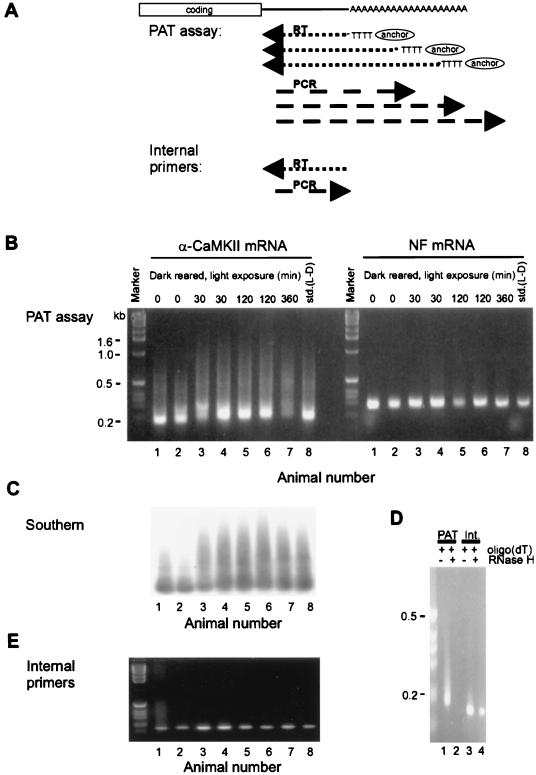
FIG. 4.
Poly(A) tail elongation in the central nervous system. (A) The method used to detect poly(A) tail length is the RT-PCR-based PAT [poly(A) test]. Here, oligo(dT) fused to a GC-rich anchor will anneal to multiple regions along the length of a poly(A) tail. When it is reverse transcribed, the resulting cDNAs will be heterogeneous in size. Following PCR with an mRNA-specific primer and the oligo(dT) anchor, the size heterogeneity will be maintained. Thus, mRNAs with long poly(A) tails will yield cDNAs of diverse sizes, the largest of which will approximate the longest poly(A) tail. On the other hand, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails will yield smaller cDNAs with discrete sizes. In addition, PCR with two mRNA-specific primers will result in products with discrete sizes (internal control). RT, reverse transcription. (B) Visual cortices were removed from rats born and raised in the dark (dark rearing) and then either not exposed to light or exposed to light for 30 to 360 min. The visual cortices were also removed from rats maintained on a standard 12-h light-dark cycle (std.). Following RNA extraction, PATs were performed for α-CaMKII mRNA, which contains a CPE, and neurofilament (NF) mRNA, which does not contain a CPE. The PATs used the same reverse transcription reaction. The products were resolved on an agarose gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. Note that the poly(A) tail of α-CaMKII mRNA was elongated in response to light, while the poly(A) tail of NF mRNA was unaffected. (C) The α-CaMKII PCR products from panel B were Southern blotted and probed with radiolabeled α-CaMKII 3′ UTR. This blot confirms that the ethidium bromide staining material in panel B corresponds to α-CaMKII sequences and also shows light-dependent polyadenylation of this mRNA. (D) An aliquot of visual cortex RNA annealed to excess oligo(dT) was incubated with RNase H, which removes the poly(A) tail. This was followed by a PAT for α-CaMKII mRNA, or reverse transcription-PCR with internal, mRNA-specific primers. This control confirms that the heterogeneously sized α-CaMKII sequences in panel B resulted from oligo(dT) priming of the poly(A) tail. (E) Reverse transcription-PCR with two α-CaMKII 3′ UTR-specific primers was performed on the same visual cortex RNA used in panel B. This control confirms that the 3′ UTR of α-CaMKII mRNA was intact, since the PCR product is discrete and has the predicted size. Reprinted from reference 109 with permission of the publisher.