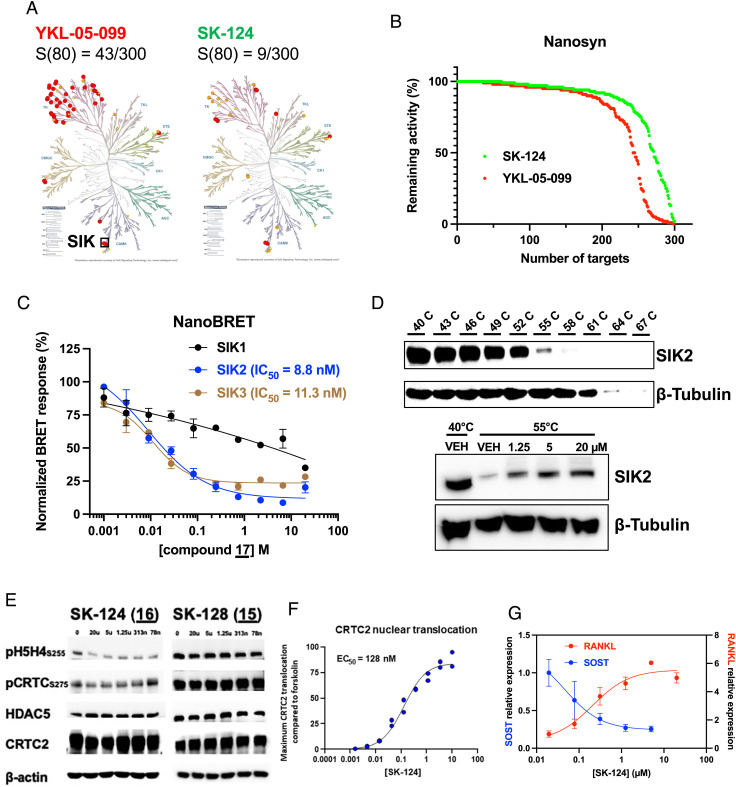
Fig. 3.
Kinome selectivity and cellular activity of SK-124. (A) YKL-05-099 and SK-124 were tested at 0.5 µM on a panel of 300 human kinases. Dendrograms show kinases inhibited >80% by each compound in red. SIK isoforms are present at the 6-o’clock position. S(80) refers to the portion of kinases tested whose activity was inhibited >80% by 0.5 µM compounds. (B) Comparison of SK-124 and YKL-05-099 against 300 kinases as percentage of remaining activity. (C) NanoBRET assays using NanoLuc–SIK fusion proteins were performed in HEK293T cells using the indicated doses of SK-124 used for cell-based calculation of IC50 values. (D) Cellular thermal shift assay was performed in Ocy454 cells. Top panels show the melting curve used to determine SIK2 thermostability. A melting temperature of 55 °C was selected for subsequent studies. Bottom panels show effects of SK-124 treatment (1 h) on SIK2 thermostability at 55 °C. (E) Ocy454 cells were treated with the indicated compounds/doses for 1 h followed by immunoblotting as indicated. (F) PathHunter® U2OS CRTC2 (TORC2) nuclear translocation reporter cells were treated for 90 min with the indicated doses of SK-124. Data are reported as CRTC2 nuclear translocation relative to forskolin (10 µM, positive control). (G) Ocy454 cells were treated for 4 h with the indicated doses of SK-124 followed by RNA isolation for RT-qPCR, with β-actin used as a housekeeping gene.