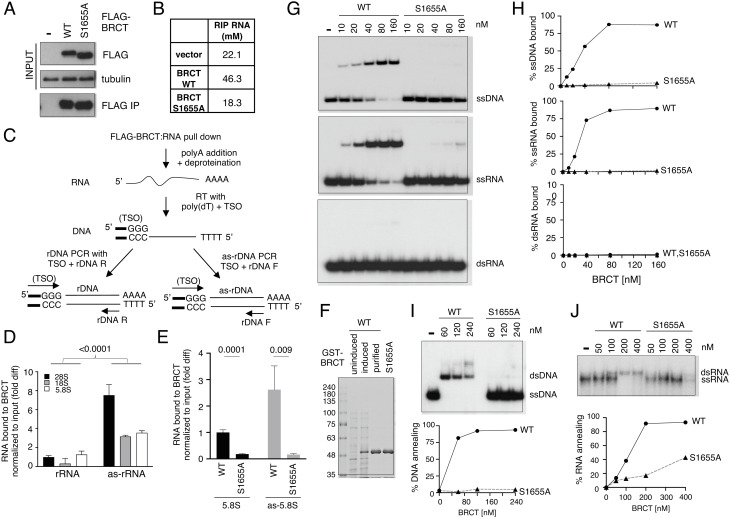
Fig. 3.
BRCA1 BRCT binds to rRNA and as-rRNA to promote dsRNA formation. (A) Western blot analysis of WT and S1655A FLAG-BRCT using an anti-FLAG antibody before (Top) and after FLAG pulldown using M2 agarose beads (Bottom). Tubulin was used as input loading control (Middle). (B) Concentrations of RNA copurified with WT and S1655A BRCT from A measured by nanodrop. (C) Schematic of BRCT RIP coupled with RT-qPCR procedure. TSO: template switch oligo. rDNA F: rDNA forward primer. rDNA R: rDNA reverse primer. (D) Quantification of rRNA and as-rRNA copurified with WT FLAG-BRCA1 BRCT normalized to input RNA measured by RT-qPCR. Y-axis represents fold difference relative to 28S rRNA bound to BRCT. (E) 5.8S rRNA (Left) and 5.8S as-rRNA (Right) copurified with either WT or S1655A FLAG-BRCA1 BRCT normalized to input RNA were measured by RT-qPCR. Y-axis represents fold difference relative to 5.8S rRNA bound to WT BRCT. (F) Recombinant WT and S1655A GST-tagged BRCA1 BRCT protein fragments overexpressed and purified from E. coli, separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. (G) Representative images of the electrophoretic mobility shift assays of WT and S1655A GST-BRCT protein fragments binding to 32P-end labeled ssDNA (Top), ssRNA (Middle), or dsRNA (Bottom) substrate. (H) Quantification of the percentage of ssDNA, ssRNA, or ssRNA bound by WT and S1655A GST-BRCT protein fragments from G by Image J. (I, Top) Representative image of DNA:DNA annealing activity of purified recombinant BRCT WT and S1655A mutant protein fragments measured using 32P-end-labeled ssDNA with complementary ssDNA oligonucleotides. Quantification of the percentage of DNA annealing by Image J was shown (Bottom). (I, Top) Representative image of RNA:RNA annealing activity of purified recombinant BRCT WT and S1655A mutant protein fragments measured using 32P-end-labeled ssRNA with complementary ssRNA oligonucleotides. Quantification of the percentage of RNA annealing by Image J was shown (Bottom).