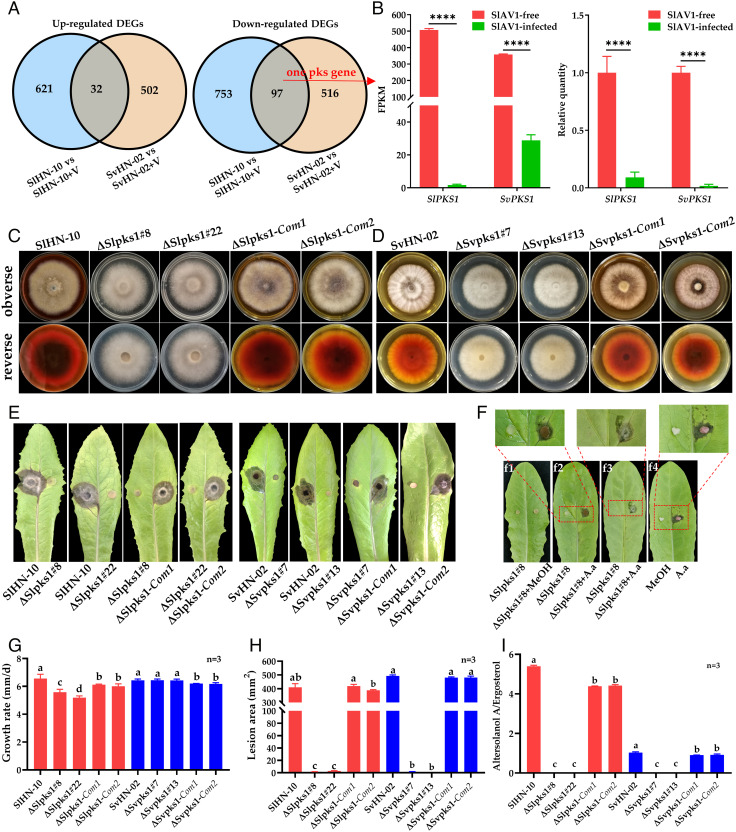
Fig. 3.
SlPKS1 and SvPKS1 are required for biosynthesis of Altersolanol A, a key pathogenic factor of S. lycopersici. (A) A comparison of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in virus-infected (+V) vs. virus-free SlHN-10 and SvHN-02 shown by Venn diagrams. (B) Expression levels of SlPKS1 and SvPKS1 based on RNA-seq and RT-qPCR. FPKM, fragments per kilobase per million mapped reads. (C) Colony morphology of the wild-type (SlHN-10), two independent SlPKS1 deletion mutants (ΔSlpks1#8 and ΔSlpks1#22), and two complemented strains (ΔSlpks1-Com1 and ΔSlpks1-Com2) grown on potato dextrose agar (PDA) for 7 d. (D) Colony morphology of the wild-type (SvHN-02), two independent SvPKS1 deletion mutants (ΔSvpks1#7 and ΔSvpks1#13), and two complemented strains (ΔSvpks1-Com1 and ΔSvpks1-Com2) grown on PDA for 7 d. (E) and (H) Virulence assay on detached lettuce leaves. (F) Symptoms on lettuce leaves inoculated with ΔSlpks1#8, ΔSlp ks1#8 added 5 μL methanol (f1) and ΔSlpks1#8 added 5 μL Altersolanol A (A.a) standards (10 μg/mL) (f2). (f3) shows the backside of f2 leaf. (f4), lettuce leaf inoculated with sterilized cotton balls soaked with 5 μL A.a standards (10 μg/mL), respectively. (G) Growth rate measurement of fungal strains on PDA. (I) Quantification of Altersolanol A production in S. lycopersici and S. vesicarium strains normalized by ergosterol levels proportional to fungal biomass. Error bars indicate SDs (n = 3). Different letters indicate the statistically significant difference by a one-way ANOVA (P < 0.05).