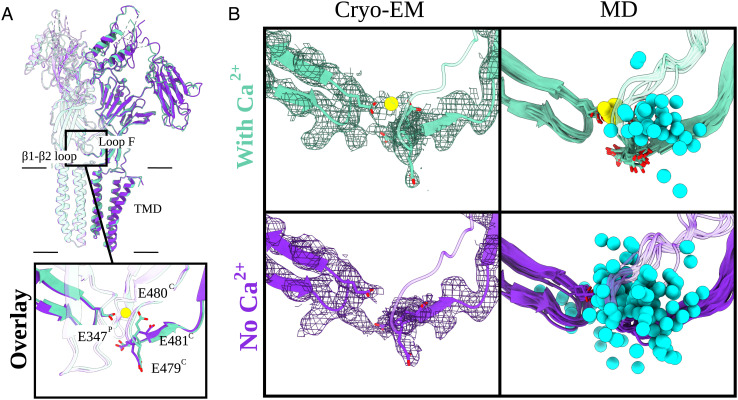
Fig. 3.
Arrangement of the calcium-binding residues elucidated by cryo-EM and MD. (A) Overlay of two adjacent subunits of DeCLIC cryo-EM structures with and without Ca2+ (aquamarine and purple, respectively). Protein domains and main Ca2+-binding motifs are shown. Those include the transmembrane domain (TMD), extracellular domain (ECD), and two amino-terminal domains (NTD1 and NTD2) as well as the β1 to β2 loop from the principal subunit (P) and loop F from the complementary subunit (C). The boxed-in view (Bottom) shows the relevant side chains (sticks, colored by heteroatom). The Ca2+ ion present in the Ca2+ dataset (aquamarine) is colored in yellow. (B) Cryo-EM panels (Left) represent the cryo-EM structures and their corresponding densities (mesh at α = 0.012 to 0.015). Relevant side chains around the Ca2+-binding site [loop F (C), β1 to β2 loop (P)] are displayed as sticks (heteroatom coloring). The density for the Ca2+-binding residues as well as for the Ca2+ ion (in the with-Ca2+ condition) is well resolved. MD panels (Right) illustrate eleven individual conformations (one snapshot for every 100 ns) from 1-μs long MD simulations of the cryo-EM models. The relevant Ca2+ residues are displayed as sticks (colored by heteroatom). In cyan, we have Na+ ions (sphere, trajectories generated for every 10 ns) and Ca2+ ion in yellow. In the no-Ca2+ condition, the Na+ ions are free to enter the cavity which is occupied by Ca2+ in the with-Ca2+ condition.