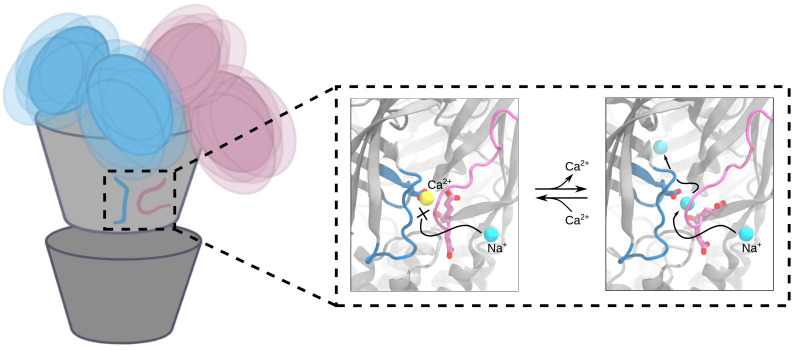
Fig. 6.
Conformational variability and proposed calcium-binding site behavior in closed DeCLIC. The positions of the N-terminal domains of DeCLIC fluctuate around the core of the protein, sampling a wide range of conformations where the average can be described by an asymmetric conformation with a mix of compact and extended NTD positions. In the calcium-binding site, bound calcium blocks sodium access to the site. Following calcium depletion, sodium can enter the central pore through the calcium-binding site. The calcium-binding site is thus proposed to act as a supplementary way for sodium ions to reach the ion conduction pathway, with the three consecutive glutamates on loop F shepherding sodium from outside the protein, through the calcium-binding site, and into the extracellular part of the ion channel pore.