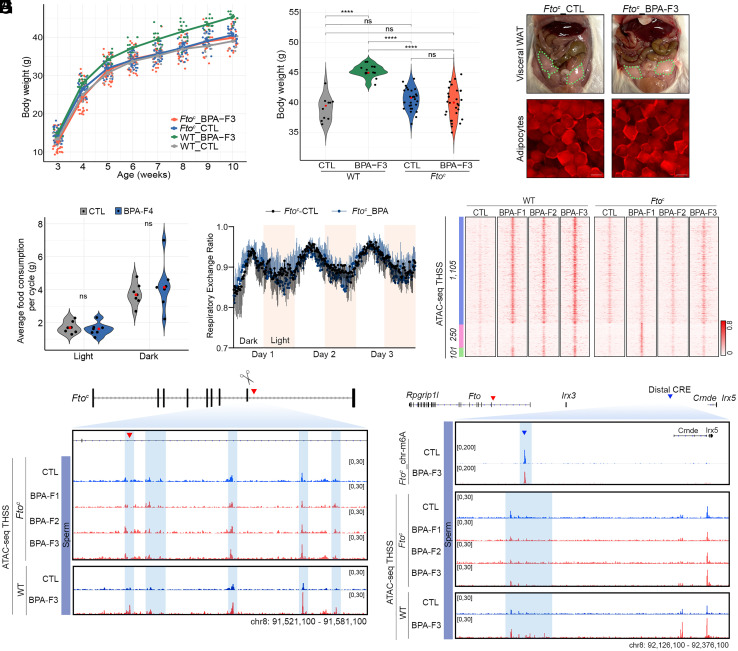
Fig. 5.
Deletion of the CTCF site in the Fto proximal CRE prevents transgenerational transmission of obesity. (A) F3 Ftoc male mice ancestrally exposed to BPA fail to gain weight with age with respect to unexposed Ftoc_CTL and WT_CTL (Ftoc_CTL n = 34, Ftoc_BPA n = 40, WT_CTL n = 15, and WT_BPA n = 15). (B) The body weight of 10-wk-old Ftoc male mice ancestrally exposed to BPA is the same as that of non-exposed Ftoc and WT males but lower than that of exposed WT males (Ftoc_CTL n = 28, Ftoc_BPA n = 30, WT_CTL n = 10, WT_BPA n = 15). (C) 10-wk-old Ftoc male mice of the F3 generation ancestrally exposed to BPA do not have excess visceral adipose tissue with respect to unexposed Ftoc_CTL (Top). Adipocytes accumulate the same amount of lipids and are the same size in unexposed and exposed Ftoc mice (Bottom). (D) Ftoc mice ancestrally exposed to BPA at 10 wk of age have the same food intake during the light and dark cycles as unexposed controls (Ftoc_CTL n = 7, Ftoc_BPA n = 7). (E) The respiratory exchange ratio, which measures consumption of stored fats versus carbohydrates from a recent meal, is the same in Ftoc male mice ancestrally exposed to BPA and unexposed controls (Ftoc_CTL n = 7, Ftoc_BPA n = 7). (F) Comparison of chromatin accessibility determined by ATAC-seq in sperm of WT and Ftoc male mice unexposed and ancestrally exposed to BPA. Most sites induced by BPA exposure in WT mice do not increase in accessibility in Ftoc mice (blue cluster). Only a small subset is induced in Ftoc BPA-F1 mice, but they return to normal in the F2 generation (green cluster). Exposure to BPA results in increased accessibility at 250 sites in Ftoc but not WT mice, suggesting that deletion of the CTCF site in the proximal enhancer alters the response to BPA. These sites do not persist to the F2 generation (pink cluster). (G) The Fto proximal CRE does not show increased chromatin accessibility and TF occupancy in the sperm of Ftoc mice ancestrally exposed to BPA compared to unexposed controls. (H) Levels of m6A in the eRNA located in the Fto distal CRE are not affected in Ftoc mice ancestrally exposed to BPA. Chromatin accessibility and TF occupancy in the Fto distal CRE is the same in the sperm of Ftoc mice ancestrally exposed to BPA compared to controls. P values were calculated as indicated in the Statistical Analyses of Metabolic Data section of Methods; ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, ns not significant (SI Appendix, Fig. S4-5 and S6).