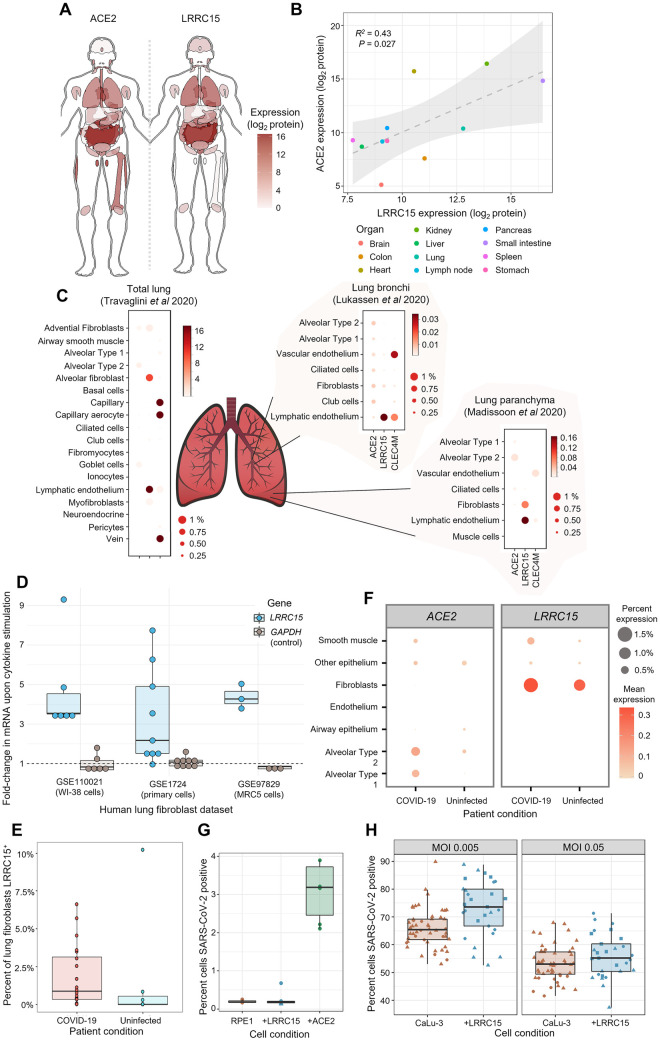
Fig 4. LRRC15 is expressed in virus-susceptible tissues and can modulate SARS-CoV-2 infection.
(A) Tissue distribution of LRRC15 and ACE2 expression based on a whole-body proteomic atlas [35]. For each tissue, protein expression is reflected by the red color intensity scale provided. (B) Organs with high ACE2 expression tend to also express substantial LRRC15. Each data point represents protein abundance in a major human organ or tissue as measured by mass spectrometry. A linear regression line and 95% compatibility interval is shaded in gray. (C) Single-cell transcriptome measurements of human lung specimens identify cell type distributions for LRRC15 expression. The percentage of cells where a gene transcript was detected is indicated by size, while average counts per cell are color-shaded. Expression of spike receptors ACE2 and CLEC4M are shown for comparison. (D) Inflammatory cytokines greatly up-regulate the expression of LRRC15 in lung fibroblasts. Three different publicly available datasets are shown that exposed cultures of human lung fibroblast cells to TGF-beta. Relative changes in mRNA expression were calculated for LRRC15 and, as a negative control not expected to change, GADPH. (E) COVID-19 patients have greater proportions of LRRC15-expressing fibroblasts in their lungs compared to uninfected patient controls. Each point is a different lung tissue donor measured in a recent single-cell RNA-seq study [49] showing the percentage of single fibroblast cells where LRRC15 mRNA was detected. (F) The lungs of COVID-19 patients experience a broad expansion in both LRRC15 and ACE2 expressing cells. For each cell population identified by single-cell RNA-seq [49], the expression (as measured both by average mRNA counts and percentages of cells) was compared between deceased COVID-19 patients and uninfected controls. (G) Expression of LRRC15 is insufficient to make cells permissive to SARS-CoV-2 infection. LRRC15 or ACE2 were overexpressed by transducing RPE1 cells with CRISPRa sgRNA followed by infection with a recombinant SARS-CoV-2-ZsGreen reporter virus. (H) LRRC15 overexpression changes the susceptibility of CaLu-3 lung cells to viral infection. CaLu-3 cells were transduced with lentiviruses to overexpress LRRC15 followed by infection with SARS-CoV-2-ZsGreen. Viral infection was quantified by counting GFP-positive cells by fluorescent microscopy in (D) and (E). ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019; CRISPRa, CRISPR activation; LRRC15, leucine-rich repeat containing protein 15; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2.