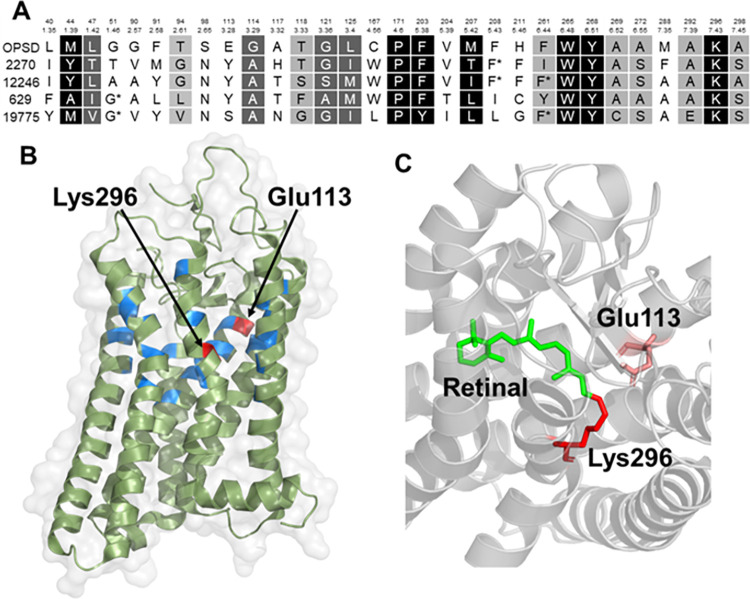
Fig 3. Sequence alignment and active site analysis of rhodopsin.
(A) Alignment of human rhodopsin with remotely homologous coral proteins, only showing the positions of those amino acids that are in proximity to the ligand in the opsin family (ref). TheBallesteros-Weinstein numbering scheme is used to enable comparison to other members of the GPCR family. Positions are colored according to the degree of similarity: White foreground/black background, 100%; white foreground/grey background, > 80%, black foreground/grey background, > 60%. (B) Active site of bovine rhodopsin crystal structure 1L9H (>99% homologous to human rhodopsin) showing the residues involved in the active site shown in (A). (C) Active site showing the interaction of the ligand and vitamin A derivative, retinal, which makes rhodopsin light-sensitive, with Lys296 and Glu113 (also labeled in A,B).