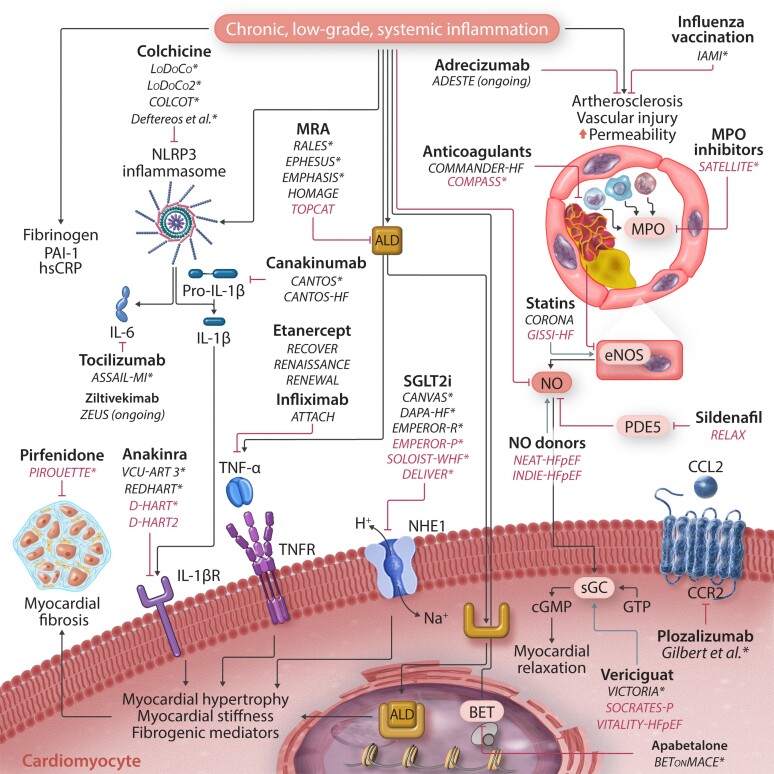
Figure 2.
Clinical trials targeting inflammatory pathways in patients with heart failure. Many different biochemical pathways are involved in inflammation-driven heart injury and can be targeted at different levels. Drugs are in bold, while clinical trials are in italics (trials that included patients with HFpEF are marked blue). ‘*’ denotes trials/studies that met their primary endpoint. BET, bromodomain and extra-terminal motif; CCL2, C–C chemokine ligand 2; CCR2, C–C chemokine receptor Type 2; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; ECM, extracellular matrix; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; IL-1β-R, interleukin-1β receptor; MPO, myeloperoxidase; NLRP3, nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptor family, pyrin domain-containing; NO, nitric oxide; PDE5, phosphodiesterase-5; sGC, soluble guanylate cyclase; TNFR, tumour necrosis factor receptor.