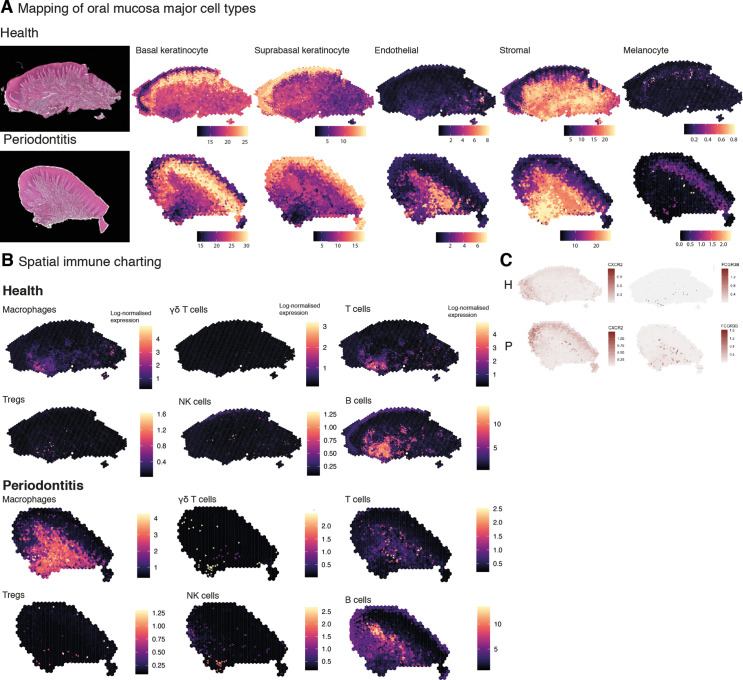
Figure 5. Mapping of oral mucosa major cell types across conditions.
(A) Spatial expression of genes encoding for main human oral mucosa cell types. We selected the top differentially expressed genes for each cell type and predicted their expression at subspot resolution xgboost in BayesSpace. H&E staining shown here for clarity. (B) Spatial mapping of immune cell types showing overall increase in disease. (C) Neutrophils mapping using expression of CXCR2 and FCGR3B.