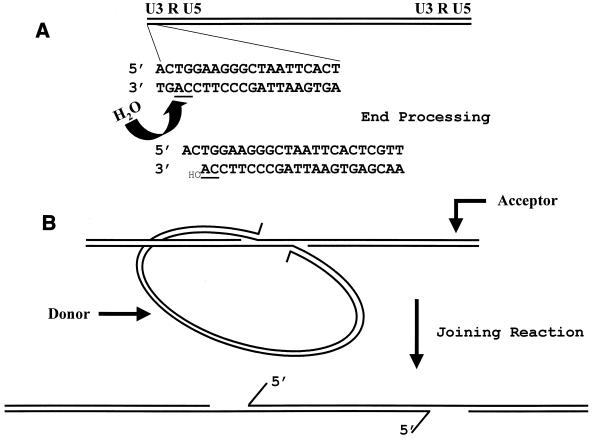
FIG. 2.
Diagrammatic representation of the mechanism of integration. (A) End-processing reaction. A viral DNA is depicted with the U3 LTR sequence on the left. Magnified below is the 20-bp sequence of the terminal HIV-1 U3 LTR. In an initial reaction, there is a loss of 2 bases from the 3′ strand, adjacent to a highly conserved CA dinucleotide (underlined), via a nucleophilic attack by a water molecule. (B) Joining reaction. The processed LTR DNA ends are brought together into a complex with the target DNA. Insertion of the donor into the target DNA involves a nucleophilic attack by using the 3′ hydroxyl groups on the exposed 3′ strand. The result is a gapped DNA with 5′ 2-base overhangs. Overhang removal, gap, and nick repair would complete the integration reaction.