Fig. 2.
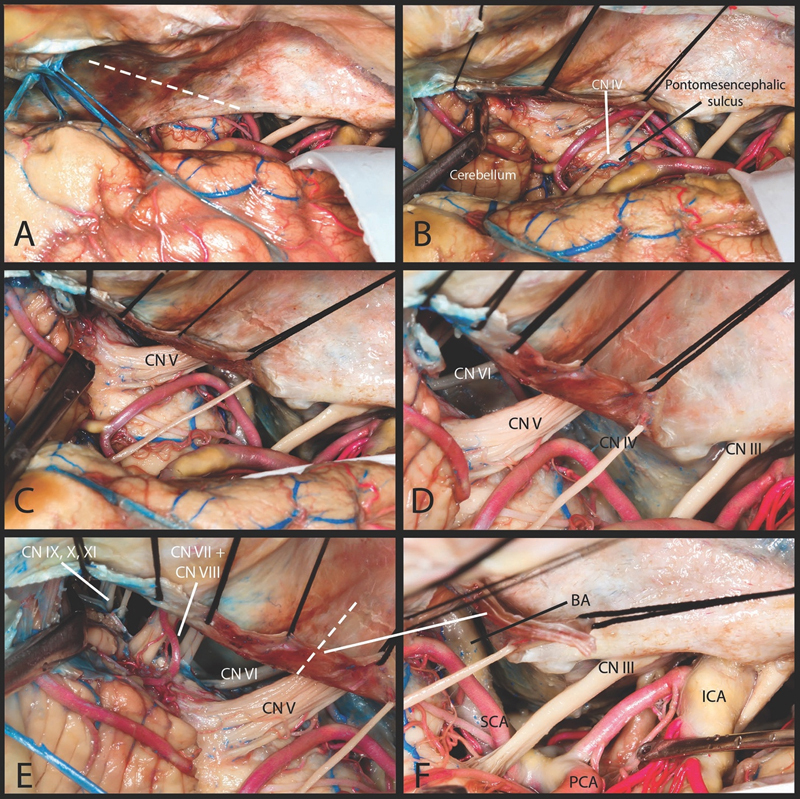
Linear technique. ( A ) The incision starts at the point just posterior to the tentorial entry point of the trochlear nerve. Incision runs parallel to the superior petrosal sinus. ( B ) This incision allows for visualization of the brain stem below the pontomesencephalic sulcus. The lateral surface of the pons can be visualized. Posteriorly the superomedial surface of the cerebellar hemisphere is also visualized. ( C ) The entry zone of the trigeminal nerve as well as its whole length within the prepontine cistern on its way to Meckel's cave is visualized. ( D ) Inferior to the trigeminal nerve the abducens nerve was identified. ( E ) Further lateral extension of the incision allows visualization of the facial, cochlear and vestibular nerves on their way to the internal acoustic meatus. More laterally retraction of cerebellum allows lower cranial nerves to be seen. ( F ) This approach can be extended by second incision which is perpendicular to the first one. CN, cranial nerve; ICA, internal carotid artery; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; SCA, superior cerebellar artery.
