Fig. 3.
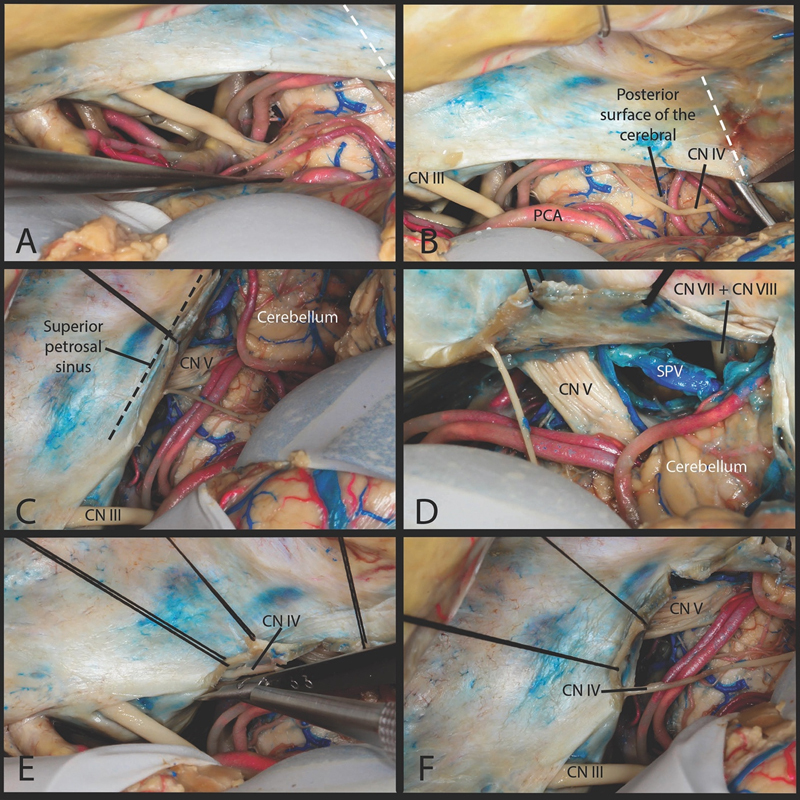
Triangular technique. ( A ) The subtemporal approach. ( B ) The incision starts from the edge of the tentorium at the level of posterior surface of the cerebral peduncle. The end point of the incision is located at the petrous ridge and superior petrosal sinus. ( C ) This creates triangular tentorial flap which is everted over the superior petrosal sinus. This part of the tentorium everted around the superior petrosal sinus obstructed the view of the prepontine cistern. ( D ) Looking laterally only a small course of the facial/cochlear nerve was visualized within the cerebellopontine angle. ( E ) To achieve maximal anterolateral reflection of the tentorial flap we dissected the trochlear nerve fully from its tentorial canal as far as its entrance into the cavernous sinus. ( F ) View after releasing the trochlear nerve from its tentorial canal. CN, cranial nerve; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; SPV, superior petrosal vein.
