Figure 3. Crystal structures of TR-bound human ClpP.
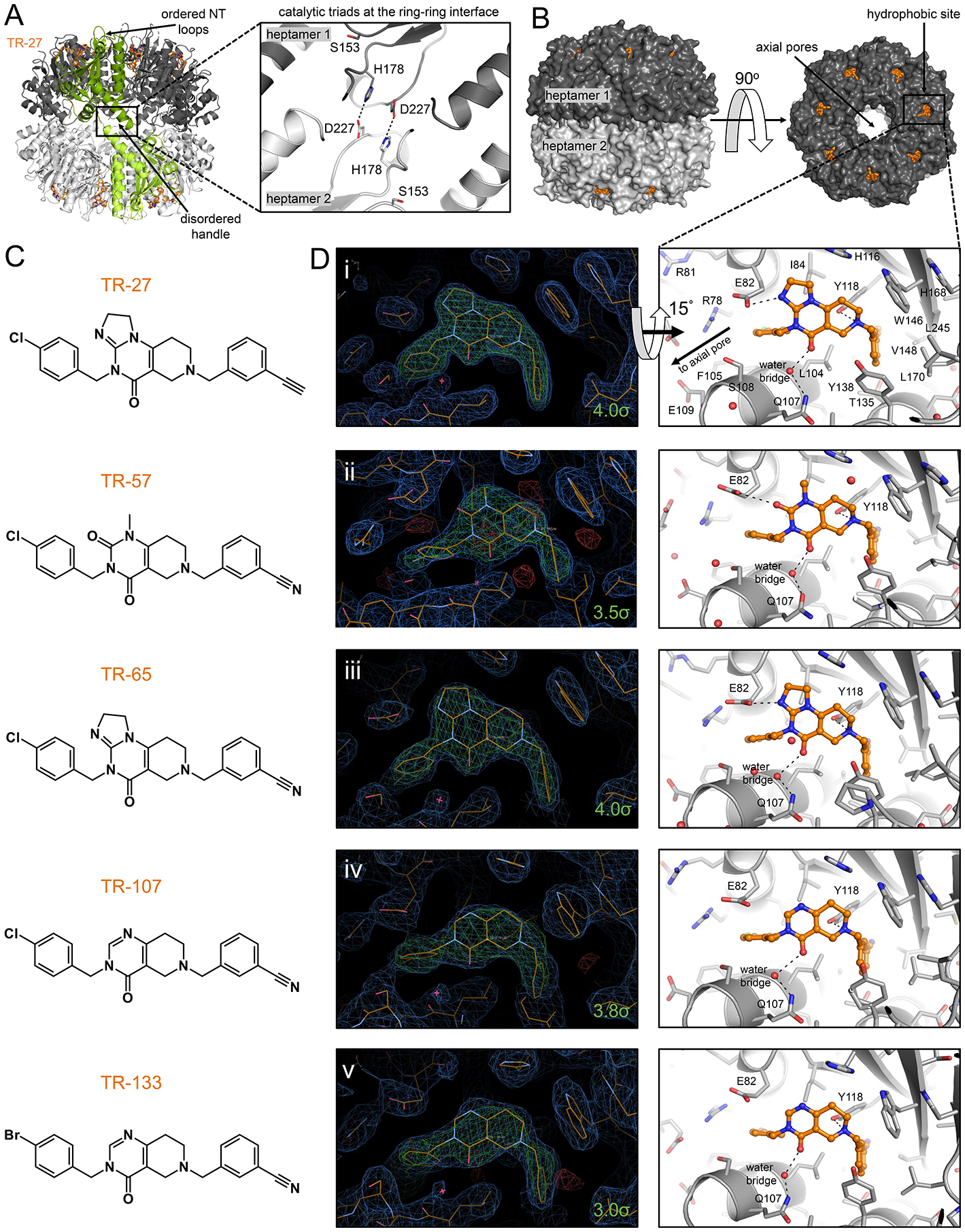
(A) The compact conformation of TR-bound ClpP featured organized N-terminal loops characteristic of the active form but shortened αE helices in the equatorial region. The catalytic triad residues H178 and D227 shown on the left as sticks formed hydrogen bonds with equivalent residues in a subunit of the opposite heptameric ring, helping stabilize the compact structure. Bound TR-27 is shown as orange sticks, and two opposing subunits are colored in green for emphasis. The two heptameric rings of human ClpP are colored in different shades of gray. The boxed area shows the general locations of the oligomerization sensors and the catalytic triads, the latter contained within. The oligomerization sensor residues E225 and R226 were disordered in the model and are not shown.
(B) Shown are side and top views of ClpP with the H-sites occupied by TR compounds drawn in orange sticks.
(C) Chemical structures of TR compounds.
(D) Left panels show electron density maps around the TR compounds that bind human ClpP H-sites in a characteristic pincer-like topology. 2Fo-Fc maps are shown in blue and are contoured at 1.0 σ, while composite omit maps are shown in green and are contoured at the indicated σ level for each molecule. Sequestered water molecules are represented by a red asterisk. Right panels are stick representations of the crystal structures, tilted by 15° along the x-axis, and show the various hydrophobic, π-stacking, and hydrogen bonding interactions with the TR compounds. Only the right panel of D(i) has the protein residues fully labeled. H-site residues that form important hydrophobic and van der Waals interactions with the TR compounds are shown as grey sticks, while those that form hydrogen bonds are indicated with black broken lines connecting to the small molecule.
