Figure 4. Activation of systemic immunity by neoadjuvant ICB.
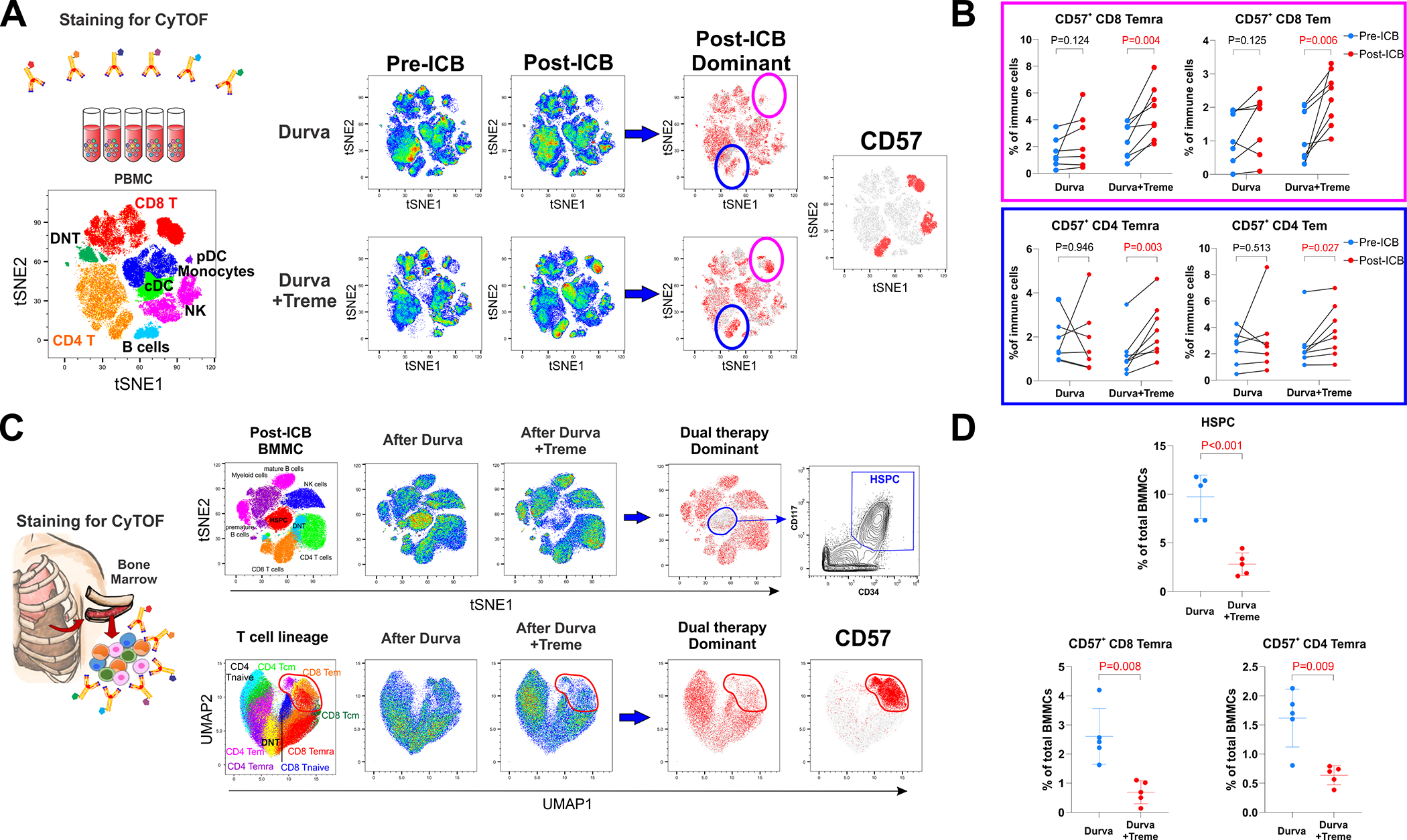
A. Dynamic changes in PBMCs after durvalumab monotherapy (n=7) and combination durvalumab plus tremelimumab (n=8). Post-ICB dominant plots compare pre-ICB and post-ICB cell populations to display major changes in cell population frequencies that occur from ICB therapy. A plot of CD57 expression on all cells is provided as a reference for the post-ICB dominant plots and together show that the two dominant cell populations that increased after combination ICB were CD8 and CD4 T cells that express CD57. B. Circulating CD57+ CD8 effector memory T cells (Tem), CD57+ CD8 effector memory T cell re-expressing CD45RA (Temra), CD57+ CD4 Tem, and CD57+ CD4 Temra increased after combination ICB. C. Bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMCs) were obtained from ribs resected for surgical exposure following durvalumab (n=5) and durvalumab plus tremelimumab (n=5). Dual therapy dominant plots demonstrate a decrease in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) and a decrease in CD57+ T cells following combination ICB. A contour plot of HSPC and a dot plot of CD57+ T cells are provided for reference. D. Combination ICB decreased bone marrow populations of cells with CD57+ CD8 Temra and CD57+ CD4 Temra phenotypes.
