Fig. 5 |. Biosynthesis model for serotonin-derived metabolites.
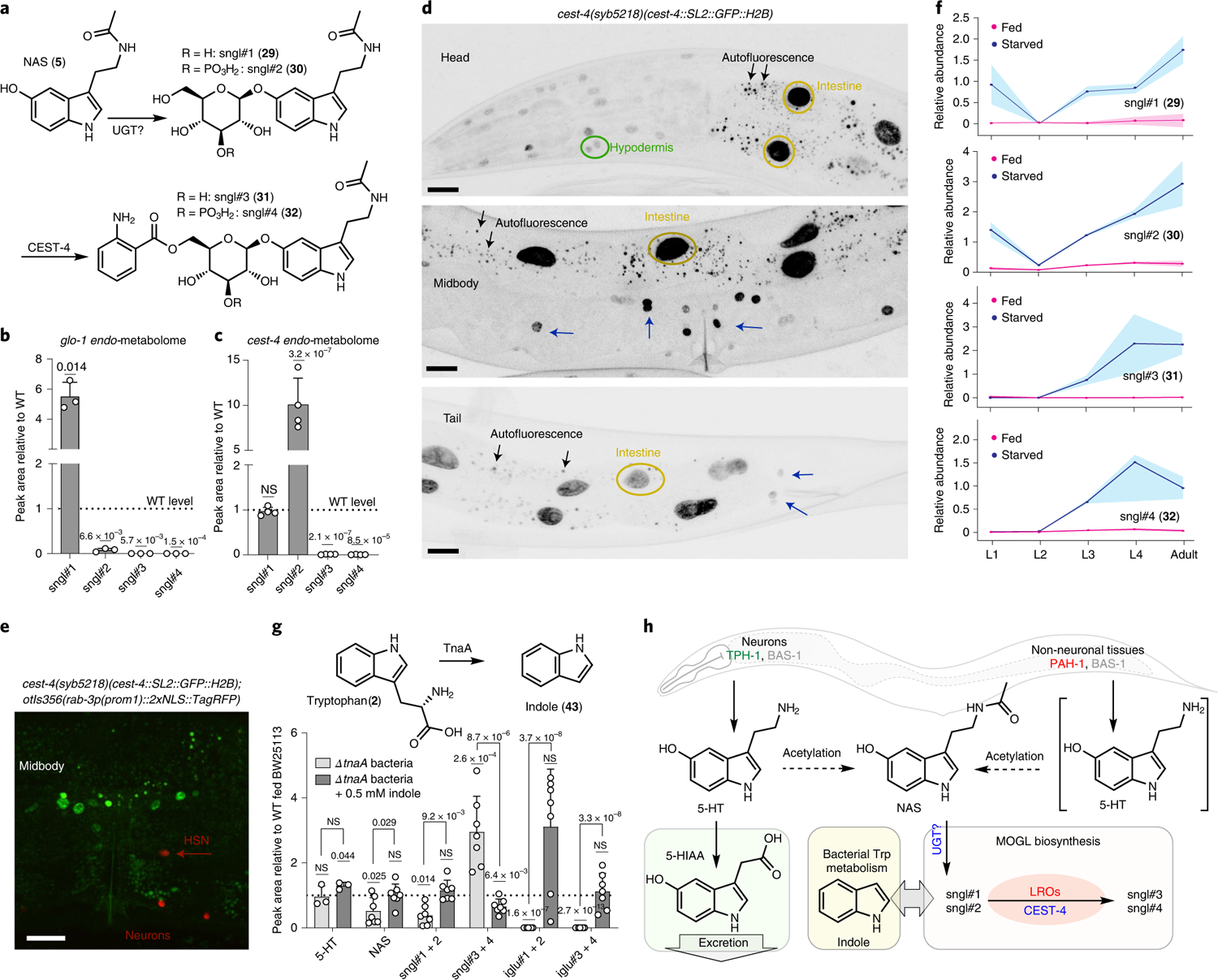
a, Proposed biosynthesis of serotonin-derived MOGLs. b,c, Serotonin-derived MOGLs sngl#3 and sngl#4 are abolished in endo-metabolomes of glo-1 (b) and cest-4 (c) animals. d, cest-4∷SL2∷GFP∷H2B is expressed in pah-1-expressing cells. Expression of cest-4 was determined using an endogenous GFP reporter (cest-4(syb5218) [cest-4∷SL2∷GFP∷H2B]). This reporter was highly expressed in the intestine (yellow circles), and in lower levels in cells in the head, including epidermal cells (green circle), as well as in cells around the vulva and in the tail (blue arrows). Scale bar, 15 μm. e, cest-4 is not expressed in any neurons (red pan-neuronal marker otIs356[rab-3p(prom1)∷2xNLS∷TagRFP]), including HSN. Scale bar, 15 μm. f, Relative abundances of sngl#1–4 in WT C. elegans in different life stages under fed and starved conditions (endo-metabolomes). g, Indole biosynthesis in E. coli affects serotonin metabolism. Relative abundances of 5-HT, sngl#1–4 in WT C. elegans fed indole-deficient ΔtnaA E. coli bacteria, with or without indole supplementation, relative to WT C. elegans fed the indole-producing parent strain, E. coli BW25113. h, Proposed model for serotonin metabolism and signaling in C. elegans. Data in b (n = 3), c (cest-4: n = 4, WT: n = 6), f (n = 3) and g (n = 7, except for 5-HT measurement, where n = 3) represent biologically independent experiments and bars indicate mean ± s.d., P values calculated by unpaired, two-tailed t-test with Welch correction; NS, not significant.
