Figure 1: Genetic targeting strategy to optogenetically manipulate Mrgprb4-lineage touch neurons.
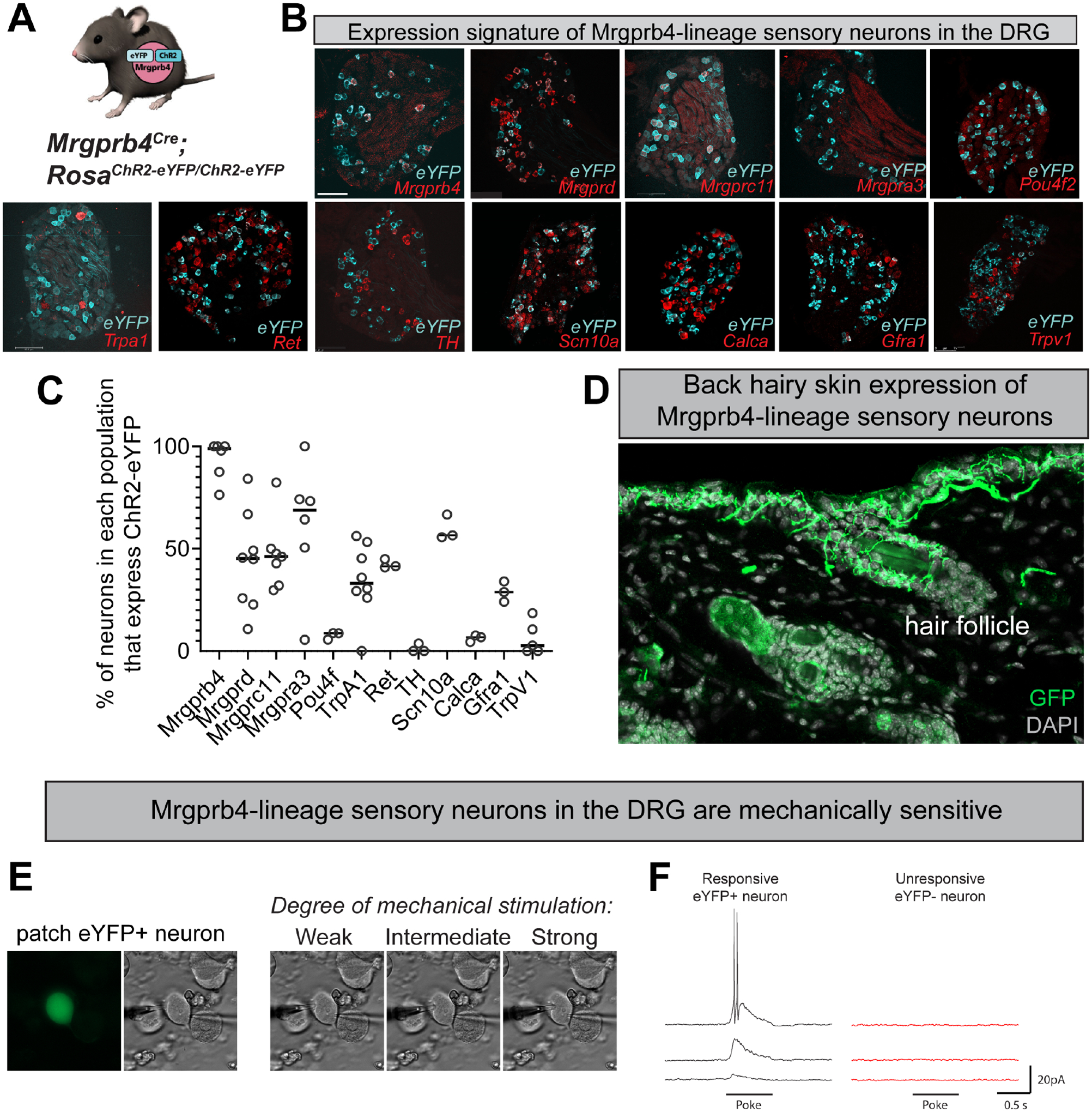
A) Mrgprb4Cre mice express ChR2-eYFP in a Cre-dependent manner. B) RNAscope in situ hybridization in DRG to quantify the expression of ChR2 in Mrgprb4+, Mrgprd+, Mrgprc11+, Mrgpra3+, Pou4f2+, Trpa1+, Ret+, TH+, Scn10a+, Calca+, Gfra1+, and Trpv1+ cells. Scale bars represent 100 μm. C) Percent expression of eYFP in different populations of DRG neurons from B. D) Expression of ChR2-eYFP in Mrgprb4-lineage nerve terminal endings in the hairy skin of the mouse back, labeled via immunofluorescence. E-F) Whole cell patch clamp recordings from individual eYFP+ Mrgprb4-lineage neurons demonstrating mechanical sensitivity. Increase in current response with increased mechanical stimulation.
