Figure 2: Mrgprb4-lineage neurons activate downstream spinal circuits including Gpr83+ spinoparabrachial projection neurons.
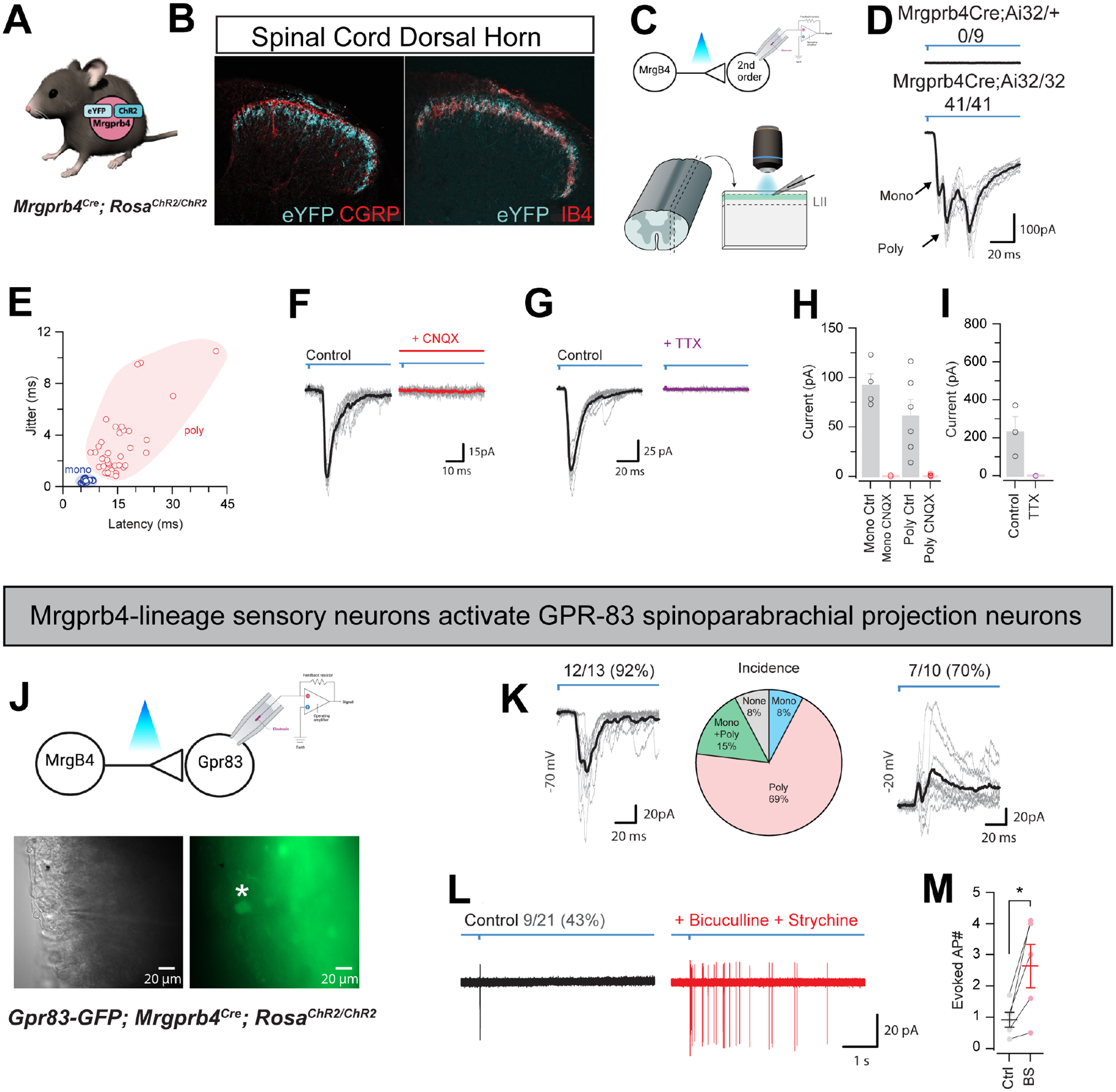
A) Mrgprb4Cre mice express ChR2-eYFP in a Cre-dependent manner. B) Immunofluorescence staining in spinal cord dorsal horn. Mrgprb4+ terminals innervate lamina II, inferior to CGRP+ terminals in lamina I and overlapping with IB4+ terminals in lamina II. Scale bars represent 100 μm. C) Schematic illustrating spinal cord slice electrophysiological recordings from lamina II during optogenetic stimulation of terminals. D) Mono- or poly-synaptic light induced currents only in Mrgprb4Cre; RosaChR2/ChR2 mice. E) Quantification of light induced currents from Mrgprb4Cre; RosaChR2/ChR2 mice with jitter used to determine mono- or poly-synaptic transmission. F) Light-induced currents in Mrgprb4Cre; RosaChR2/ChR2 mice are abolished with CNQX. G) Light-induced currents are abolished in Mrgprb4Cre; RosaChR2/ChR2 mice with TTX. H,I) Quantification of data presented in F,G. J) Schematic, brightfield, and fluorescent images illustrating recording from GFP+ GPR83+ neurons during optogenetic stimulation of Mrgprb4-lineage neurons. K-M) Characterization of light-induced inputs to Gpr83+ putative spinoparabrachial projection neurons. K) Left: Whole-cell voltage clamp recording at −70 mV demonstrating excitatory inputs, Middle: Incidence of a monosynaptic only, polysynaptic only, or mono + polysynaptic excitatory input, Right: Whole-cell voltage clamp recording at −20 mV demonstrating inhibitory inputs. L) Cell-attached recording showing light-evoked action potential discharge under normal conditions (left) and following addition of bicuculline and strychnine (right). M) Quantification of data presented in L.
