Table 3. Origin mapping methods.
Table and figure motifs show many methods to map origins of DNA replication in cell populations and in single cells or molecules96.
| Method | Description | Cite | Comments | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
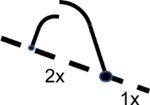
| 2D gel assays and fork direction analysis | Uses distinct gel migration patterns to characterize replication intermediates and detect origin firing efficiency | Brewer and Fangman117 Huberman et al., 118 | Pooled data using population cells |
|
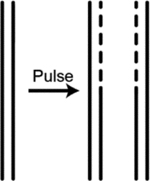
| Density transfer | Uses density isotypes to distinguish newly synthesized DNA form parental DNA followed by DNA sequencing and quantitative copy number profiling to map general patterns of replication timing | Gilbert,84; Pope et al., 14; Rhind and Gilbert6. |
|
|
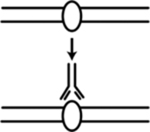
| ChlP-seq (chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by DNA sequencing) | Identify locations of ORC and MCM binding sites to predict the location of replication origins | Belsky et al., 256; Long et al., 214; Lucas and Raghuraman,257; MacAlpine et al190,258 |
|
|
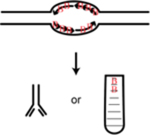
| Bubble-seq | Trap replication bubbles and sequence DNA | Mesner et al., 259 |
|
|
| Ini-seq (initiation site sequencing) | Label nascent DNA with DNA analogs and either immuno-precipitate the labeled nascent DNA or separate the labeled nascent DNA from unreplicated DNA using density difference | Guilbaud et al., 107; Langley et al., 260. |
|
|
| OK-seq (Okazaki-fragment sequencing) | Isolate and sequence Okazaki fragments to map replication fork direction in asynchronous population of cells | Petryk et al., 82. |
|
|
| Repli-seq | Label nascent DNA with BrdU; look for the enrichment of BrdU-immunoprecipitated DNA in late S phase cells compared to early S phase cells | Zhao et al., 158. |
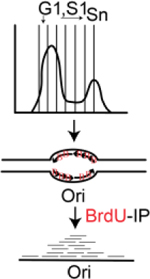
|
|
| SNS-seq (Short Nascent Strand-sequencing) | Identify nascent RNA-primed DNA synthesized at origins by the primase DNA polymerase a (Pol a) | Besnard et al., 261; Cadoret et al., 157; Cayrou et al., 262; Picard et al., 263 |
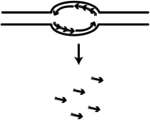
|
|
| S-jump based computational origin prediction | S-jump based method which computes the excess G over C and T over A along one DNA strand where abrupt changes correlate with the location of replication origins (N-domains and U-shaped domains of skew jumps), however the location of actual origins needs experimental validation | Brodie et al., 264. | Computational prediction data using population cells |
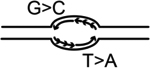
|
| Electron microscopy and fiber autoradiography | Visually observation of replication origins on radiolabeled DNA | Single molecule data using population cells |
|
|
| DNA combing | Fluorescently label nascent DNA. DNA molecules stretched and aligned along a slide and visualized by various fluorescence microscopy techniques | Bensimon et al., 265; Michalet et al., 266; Pasero et al.267. |
|
|
| DNAscent; FORK-seq etc. | Nanopore sequencing based methods that detect DNA analog labeled nascent DxwNA | Hennion et al., 268; Muller et al., 269; Georgieva et al., 270; Boemo271 |
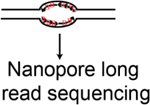
|
|
| ORM (optical replication mapping) | Fluorescent nucleotide analog pulse-labeled nascent DNA in combination with the optical mapping method (Bionano Genomics) to map long individual DNA molecules | Wang et al., 109 |
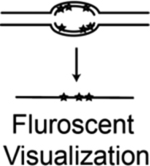
|
|
| scRepli-seq | Uses a commercial whole genome amplification kit, SeqPlex from Sigma, to prepare sequencing libraries | Miura et al., 272; Takahashi et al., 273. | Single cell data |
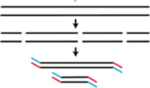
|
| LIANTI (Linear Amplification via Transposon Insertion) | Combines the T7 in vitro transcription to the Tn5 transposition to avoid the intrinsic limitations of Tn5 transposition being symmetric and reduce biases and errors during the amplification steps | Chen et al., 274 |
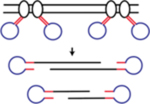
|
|
| DLP (direct library preparation) | Uses nanoliter-volume reactions to adapt the conventional transposase-based library construction to single cells | Laks et al., 275; Zahn et al., 276. |
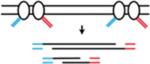
|
