Figure 1.
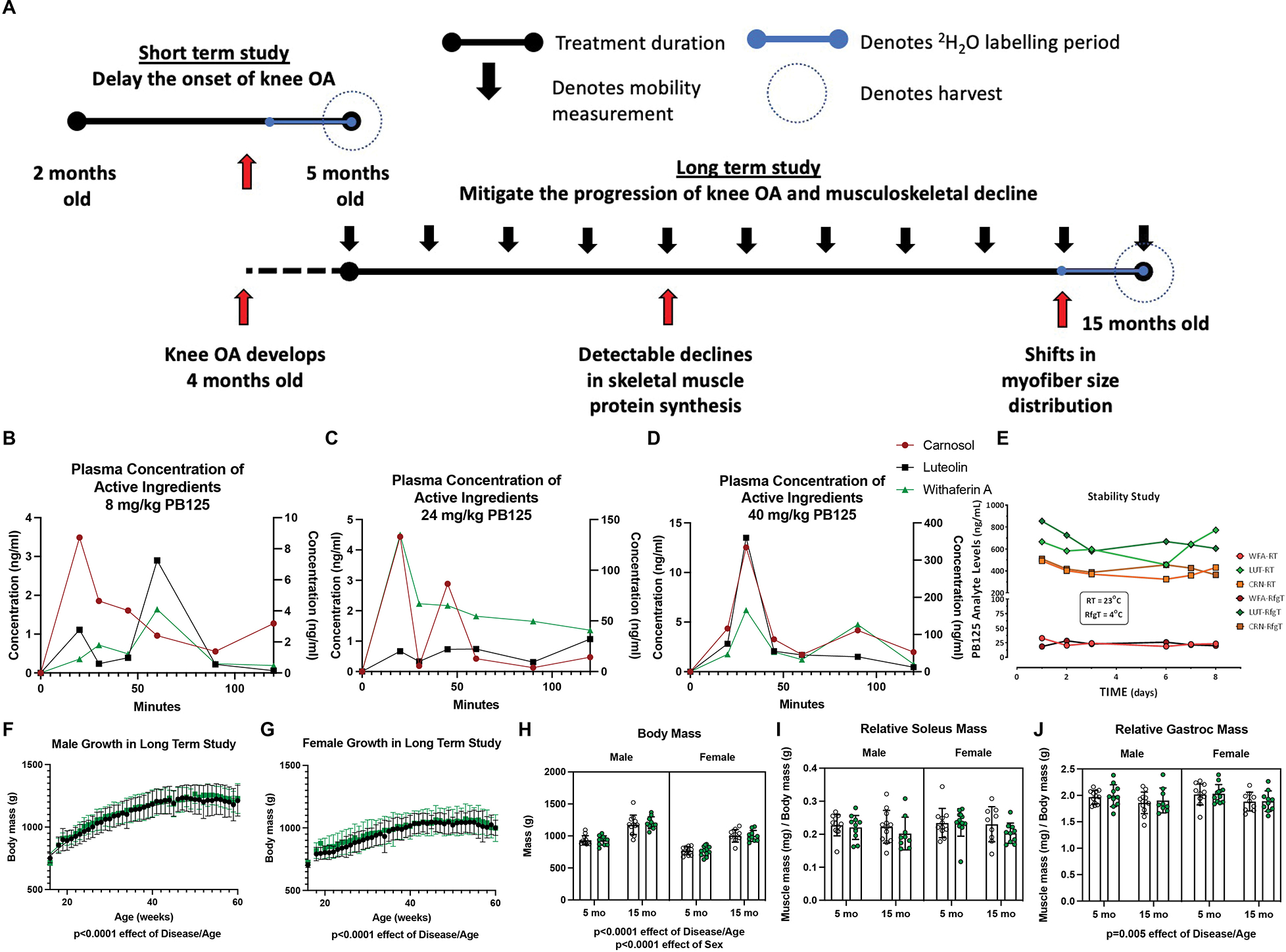
Study Design, PB125 plasma concentration, and anthropometric data. There were two cohorts of guinea pigs in this study (A). The first cohort was treated with PB125 or vehicle control from 2 mo to 5 mo, an age range during which knee OA begins developing. The second cohort was treated from 5 mo to 15 mo of age, an age range after the onset of knee OA and during which detectable declines in musculoskeletal quality arise. In the final 30 days of each study, a bolus I.P. injection of 2H2O was administered and 2H2O was mixed in drinking for measurement of protein synthesis. A portion of the soleus was harvested for mitochondrial respirometry assessments. Another portion of the soleus as well as a portion of the gastrocnemius was harvested for isotopic measurements. Comparisons between 5 mo and 15 mo guinea pigs were made between the cohorts at the day of harvest. Longitudinal weight and mobility data were acquired from the second cohort. The plasma concentrations of luteolin, carnosol, and withaferin A after dosing guinea pigs with 8 (B), 24 (C), or 40 (D) mg/kg of PB125 from 0 to 120 min. The plasma concentrations of luteolin and withaferin A are on the primary Y-axis and carnosol is on the secondary Y-axis. The stability of the phytochemical components suspended in OraSweet vehicle at room temperature and in 4°C (E). Growth charts for male (F) and female (G) guinea pigs (n=28 for each sex). There was a significant effect of Disease/Age (p<0.0001) and Sex (p<0.0001) on guinea pig body mass (n=88) (H). There was no effect of Disease/Age in relative soleus mass (mg of muscle/g of body mass) (n=86) (I); however, there was a significant (p=0.005) negative effect of Disease/Age on the gastrocnemius (n=86) (J)
