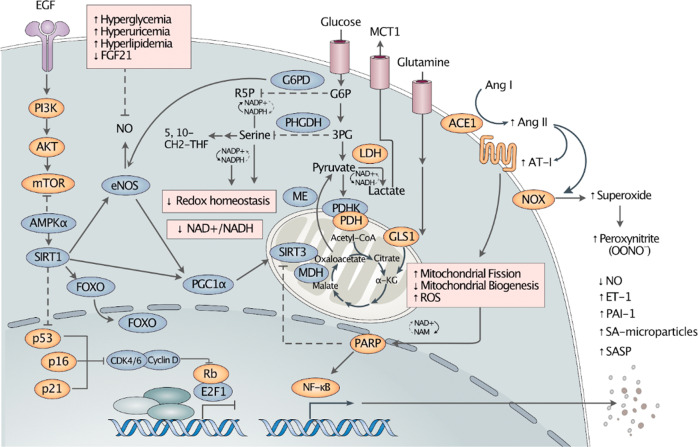
Fig. 2. Altered pathways in endothelial senescence.
We have marked proteins with activities that are believed to be reduced and increased in orange and blue, respectively. A prominent feature of endothelial senescence (ES) is impaired redox homeostasis with reduced antioxidant capacity. Senescent cells exhibit decreased NAD+/NADH levels, which may reduce ROS defense capacity. It has been suggested that potential alterations observed in ES can be summarized by the following: (1) active aerobic glycolysis driven by the activation of LDH and attenuated ME and MDH; (2) decreased PDHK activity leading to activated PDH, causing a shift to the TCA cycle; and 3) decreased PHGDH and G6PD activity leading to disruption of serine synthesis and of pentose phosphate pathway activity, respectively, and resulting in a decreased glutathione level and NADPH synthesis rate. Increased glutamine metabolism, along with an increased GLS1 level, may provide energy for senescent cells. Increased ACE, Ang II, and AT-1 activity can lead to reduced mitochondrial biogenesis and increased mitochondrial fission and ROS production. Impaired mitochondrial function can activate PARP to repair mitochondria. PARP regulates NF-κB, leading to SASP production. In ES, activated NOX may produce superoxide, which forms peroxynitrite with NO, resulting in a positive feedback loop that increases ROS and further decreases NO. EGF epidermal growth factor, PI3K phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, AMPK adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, SIRT sirtuin, FOXO forkhead box O, PGC1α peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-coactivator 1α, CDK cyclin-dependent kinase, E2F1 E2F transcription factor 1, NF-κB nuclear factor-kappa B, PARP poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, NAD nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NAM nicotinamide, NADH nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrogen, NADP nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, NADPH reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, NOX NADPH oxidase, AMP adenosine monophosphate, ADP adenosine diphosphate, ATP adenosine triphosphate, ROS reactive oxygen species, MDH malate dehydrogenase, α-KG α-ketoglutarate, GLS1 glutaminase 1, PDH pyruvate dehydrogenase, PDHK pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, ME malic enzyme, LDH lactate dehydrogenase, PHGDH D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, 5 10-CH2-THF 510-methenyltetrahydrofolate, 3PG 3-phosphoglycerate, G6P glucose 6-phosphate, G6PD glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, R5P ribose 5-phosphate, MCT1 monocarboxylate transporter 1, ACE1 angiotensin-converting enzyme 1, ANG angiotensin, AT-1 angiotensin II type-1 receptor, NO nitric oxide, ET-1 endothelin-1, PAI-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, SA senescence-associated, SASP senescence-associated secretory phenotype, eNOS endothelial nitric oxide synthase, FGF21 fibroblast growth factor 21.