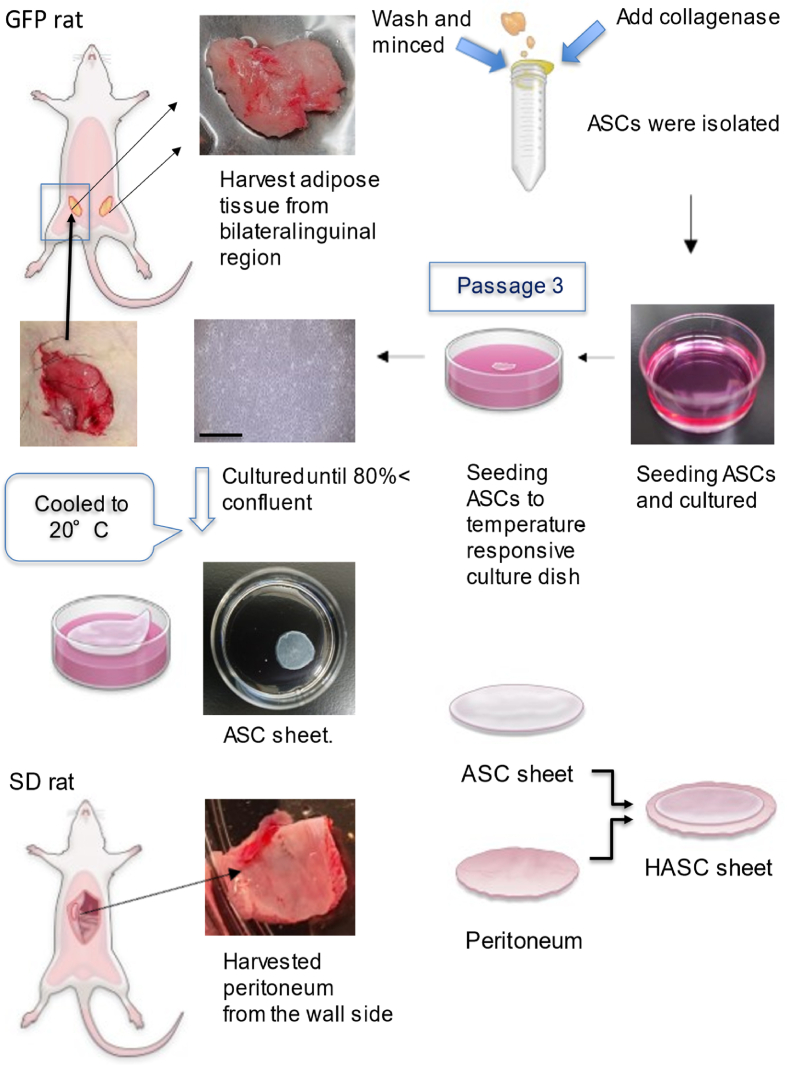
Fig. 1.
Preparation of adipose-derived stem cell (ASC) sheets and hybrid adipose-derived stem cell (HASC) sheets.
First, the adipose tissue was harvested from the bilateral inguinal region of green fluorescent protein-expressing transgenic rats. Then, collagenase was added to the finely minced adipose tissue, and the tissue was shaken for 2 h and then separated using a cell strainer. ASCs pelleted by centrifugation were seeded in Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. The cells were cultured and passaged upon reaching 80% confluency. At the third passage, the cells were seeded onto 35-mm temperature-responsive culture dishes and cultured in complete medium. After 24 h, the medium was changed, and ascorbic acid was added to the medium. The cells were cultured until reaching 90% confluency. Taking advantage of the characteristics of cell sheet engineering, the temperature-responsive culture dishes were placed in an incubator at 20 °C for 20 min to allow the cell sheets to detach spontaneously. The bottom row shows the process of making HASC sheet. Under inhalation anesthesia, the wall-side peritoneum of SD rats was removed. Since a cell sheet prepared in 35-mm temperature-responsive culture dishes were less than 30 mm in diameter, the excised peritoneum was trimmed into a circle of 35 mm diameter, and the ASC sheet was layered onto it.