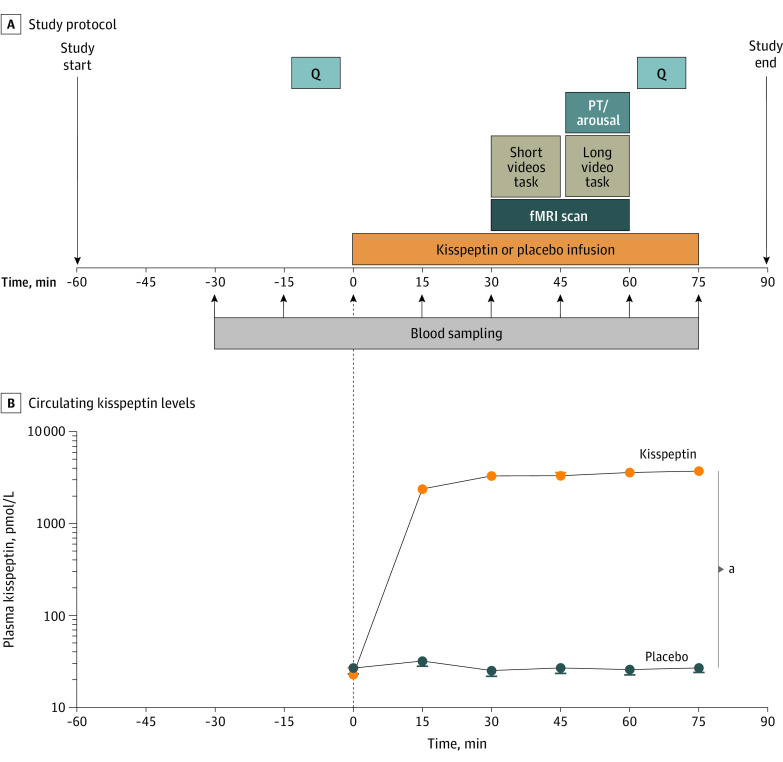
Figure 1. Experimental Protocol and Effects of Kisspeptin on Circulating Kisspeptin Levels.
A, Thirty-two men with hypoactive sexual desire disorder completed this double-blind, 2-way crossover, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. They attended 2 study visits at least 7 days apart, in balanced random order. One visit was for intravenous administration of kisspeptin-54 (1 nmol/kg/h), and the other was for an equivalent volume of placebo for 75 minutes. At each visit, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) was performed, with participants completing short and long sexual video tasks. The short videos task consisted of participants watching 20-second sexual videos (depicting heterosexual couples engaging in sexual intercourse), alternating with control nonsexual segments (involving 1 woman and 1 man exercising). The long video task consisted of participants watching a continuous 8-minute video depicting a heterosexual couple engaging in sexual activities, during which objective sexual arousal data (penile tumescence [PT]) and the subjective level of arousal were recorded. Participants completed psychometric questionnaires (Q) before and during kisspeptin and placebo administration. B, Kisspeptin administration resulted in increased circulating kisspeptin levels, reaching a plateau at 30 minutes. Therefore, circulating kisspeptin levels were stable during fMRI and intrainfusion psychometric assessments. Data depict the mean (SEM).
aP < .001 (2-way analysis of variance).