Figure 4. Effects of Kisspeptin (KP) on Sexual Brain Activity During the Long Sexual Video Task as Subjective Arousal Increased and Behavioral Parameters of Sexual Desire and Arousal.
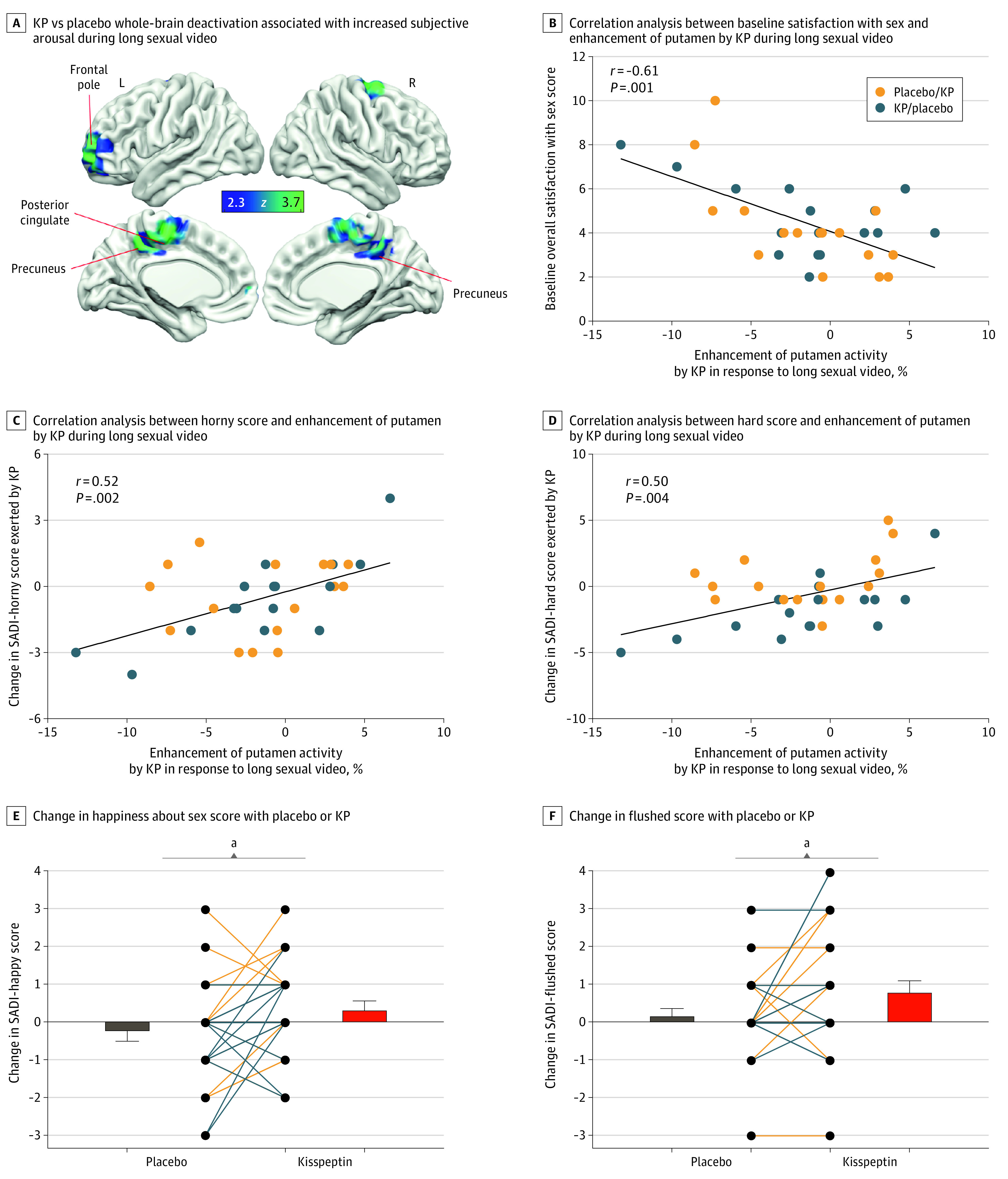
A, Whole-brain analysis showing decreased activity in the left frontal pole, right posterior cingulate cortex, and bilateral precuneus by KP administration in response to the long sexual video as subjective arousal increased. Blue and green areas show deactivation as subjective arousal increased during KP administration compared with placebo. Clusters are corrected for multiple comparisons (z = 2.3; P < .05 for all comparisons; N = 32). L indicates left; R, right. B, Correlation analysis. Participants with lower baseline satisfaction with sex showed greater KP-enhanced brain activity in the putamen in response to the long sexual video. B through F, Placebo/KP depicts the 16 participants who received placebo at the first study visit and KP at the second; KP/placebo depicts the 16 participants who received KP at the first study visit and placebo at the second. C, The more KP enhanced putamen activity, the more “horny” the participants felt in response to the long sexual video. D, The more KP enhanced putamen activity, the more “hard” the participants felt in response to the long sexual videos. E and F, Score changes for each participant show that kisspeptin administration significantly increased participant-reported happiness about sex (E) and flushing (F) compared with placebo.
aP = .02 (paired 2-sided t test).
