Figure 6.
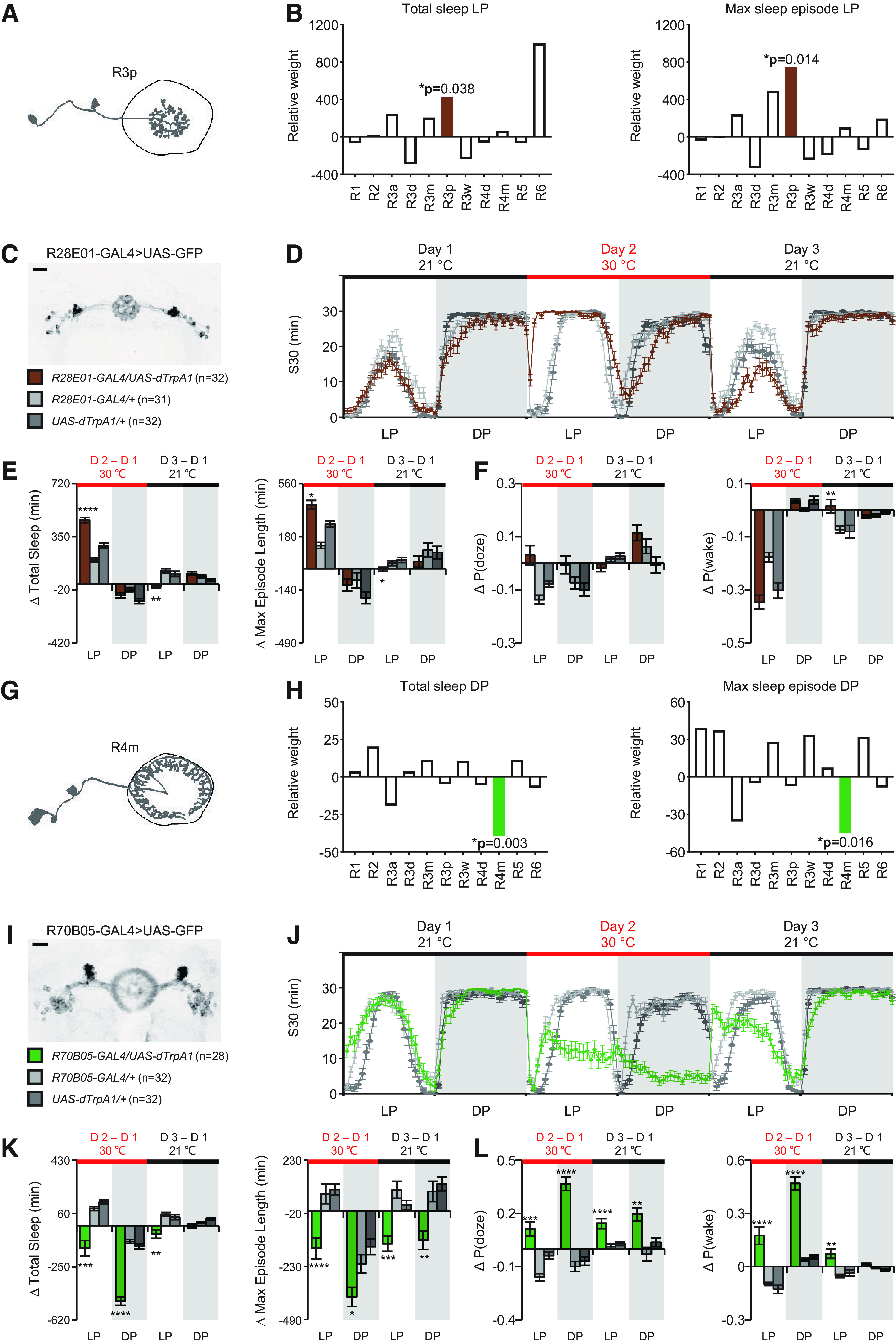
Two subtypes of ring neurons identified by GLM that significantly contribute in the regulation of total sleep and episode length. A, G, Schematic morphologic pattern of a single R3p neuron and R4m neuron, respectively. B, H, R3p neuron and R4m neuron are highly correlated to regulate daytime sleep and nighttime sleep, respectively. The weight of each subclass was analyzed with a GLM. C, I, Expression pattern of R28E01-GAL4 and R70B05-GAL4 as representative for R3p and R4m. D, J, Sleep profiles of total sleep before, during and after activation of R28E01-GAL4+ and R70B05-GAL4+ neurons with two controls. E, K, Changes in total amount of sleep and maximum episodes on the activation day and the recovery day. R70B05-GAL4+ neurons not only significantly reduced nighttime sleep but also exhibited strong impact on reducing daytime sleep. F, No detectable changes in P(doze) on and after activation of R28E01-GAL4+ neurons. Weak elevation of P(wake) on the recovery day was found. L, Strong increase in P(doze) was found when R70B05-GAL4+ neurons were activated, and this effect lasted with cessation of activation. Significant increase in P(wake) was also observed on and after activation. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. ****p < 0.0001. Data are mean ± SEM. Scale bar: 20 μm.
