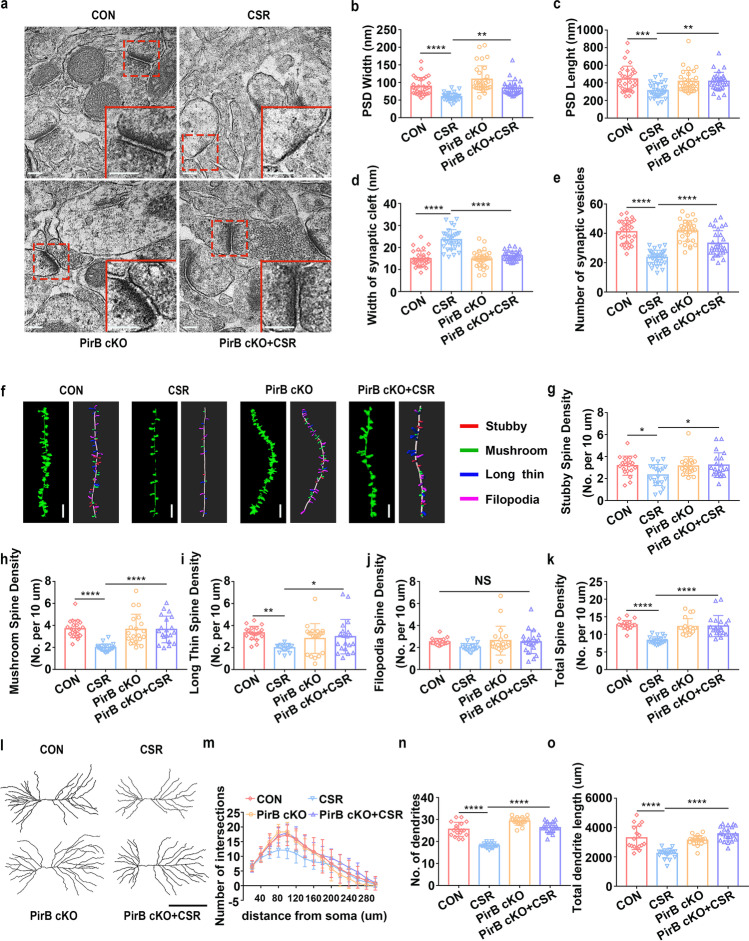
Fig. 3.
Effect of knockdown of PirB in the hippocampal CA1 region on synaptic structural deficits in CSR mice. a TEM study of ultrastructural features of synapses in the hippocampal CA1 region in control and CSR mice in the presence or absence of PirB. Scale bars: 200 nm. b The width of the PSD (n = 30–31). c The length of the PSD (n = 30–31). d The width of the synaptic cleft (n = 30–31). e The number of synaptic vesicles (n = 30–31). f Representative confocal stack and 3D reconstruction images of dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons obtained from four groups of mice. Scale bars: 5 μm. g–k Summary of the density of stubby (n = 20)-, mushroom (n = 20)-, long thin (n = 20)-, filopodia-shaped spines (n = 20), and the total spine density (n = 20) on dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons of four groups of mice. l Representative images of pyramidal neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region derived from the four groups of mice. Scale bars: 100 μm. m Sholl’s analysis of the dendritic branching complexity of the four groups of mice (n = 17–21). n, o Sholl’s analysis of total dendritic length and number of dendrites of four groups of mice (n = 17–21). Data from b–e, g–k, n, and o are presented as the means ± SD and were analysed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. Data from m are presented as the means ± SD and were analysed by two-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001)