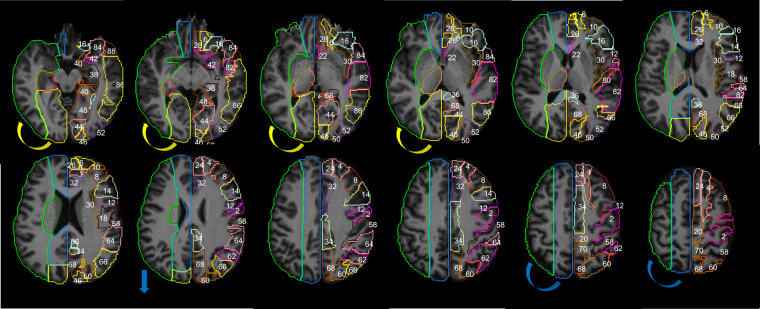
Fig. 11.
The JHU_MNI_SS template25 and the Automated Anatomical Atlas, AAL33, are used to display anatomic information in the supratentorial brain: z = 58, 64, 70, 76, 82, 88, 94, 100, 106, 112, 118, 124 mm. The numbers in the left hemisphere represent the following areas, from the AAL: 2. precentral, 4. dorsolateral superior frontal (GFs), 6. orbital superior frontal (GFso), 8. middle frontal (GFm), 10. orbital middle frontal (GFmo), 12. opercular inferior frontal (GFio), 14. triangular inferior frontal (GFit), 16. orbital inferior frontal (GFi), 18. rolandic operculum, 20. supplementary motor, 22. olfactory cortex, 24. medial superior frontal (GFds), 26. medial orbital superior frontal (GFdo), 28. rectus gyrus, 30. insula, 32. anterior cingulate and paracingulate, 34. median cingulate and paracingulate, 36. posterior cingulate, 38. hippocampus, 40. parahippocampus, 42. amygdala, 46. cuneus, 48. lingual (Gol), 50. superior occipital (GOs), 52. middle occipital (GOm), 54. inferior occipital (GOi), 56. fusiform (FG), 58. postcentral, 60. superior parietal (GPs), 62. inferior parietal (Gpi), 64. supramarginal (GSM), 66. angular (GA), 68. precunues (PreCu), 70. Paracentral lobule, 80. Hershel gyrus, 82. superior temporal gyrus (GTs), 84. superior temporal pole (GTps), 86. middle temporal gyrus (GTm), 88. middle temporal pole (GTpm), 90. inferior temporal (GTi). The colors in the right hemisphere are the major arterial territories as define by the present Atlas. The color code follows sections I-XII in Tatu et al.6, for easy comparison: ACA in blue, MCA in green, PCA in yellow. The arrows represent the main differences from Tatu et al.: the lateral inferior extension of PCA (yellow) and the lateral superior extension of ACA (blue) are larger in Tatu et al. Atlas, compared to ours.