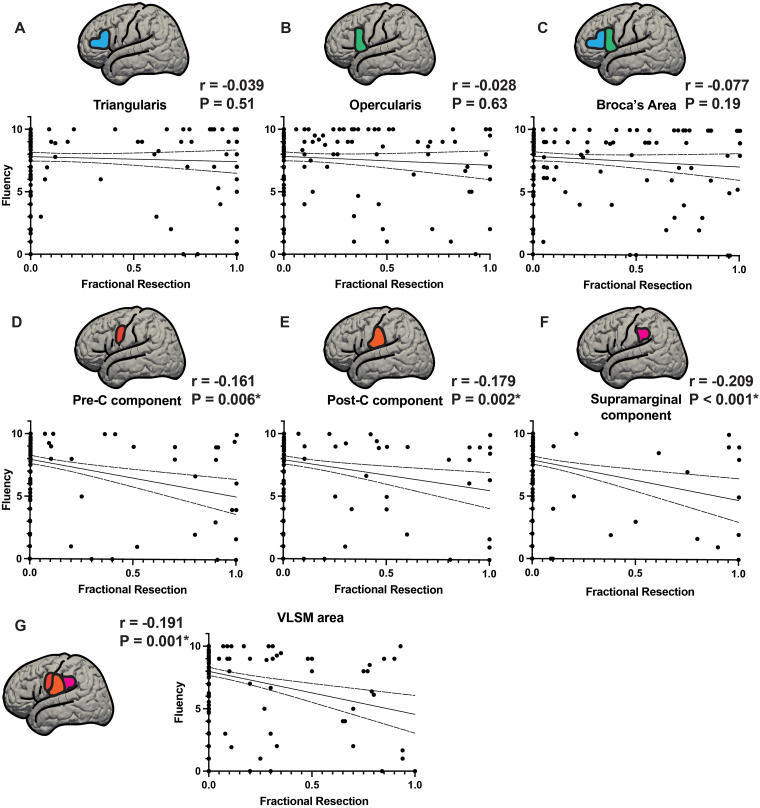
FIG. 6.
Fractional resections of Broca’s area and VLSM area gyral components versus fluency score. Resections of Broca’s area and the VLSM area were parsed into their component gyri and quantified based on the estimated fractional resection (from 0 = no involvement to 1 = total resection of the component in that gyrus) of each component. Broca’s area was divided into pars triangularis and pars opercularis and the VLSM area was divided into its components within precentral, postcentral, and supramarginal gyri. Fluency scores are plotted on the y-axis and fractional resections (0 = no resection, 1.0 = complete resection) on the x-axis. A–C: Components of Broca’s area, pars triangularis (A) and pars opercularis (B), with the fractional resections of Broca’s area as a whole (C). None of these showed significant correlations of fluency with fractional resection (A: p = 0.51, B: p = 0.63, C: p = 0.19). D–F: Fractional resections of the components of the VLSM area: precentral gyrus component (D), postcentral gyrus component (E), and supramarginal gyrus component (F). G: The VLSM area resection as a whole is shown. All 3 subcomponents of the VLSM area as well as the VLSM area treated as a whole were significantly correlated with reduced fluency (D: p = 0.006, E: p = 0.002, F: p < 0.001, G: p = 0.001). *Statistically significant at p < 0.05. Post-C = postcentral gyrus; Pre-C = precentral gyrus.