Figure 5. Effects of retigabine (RTG) on M-currents of hippocampal PV-INs.
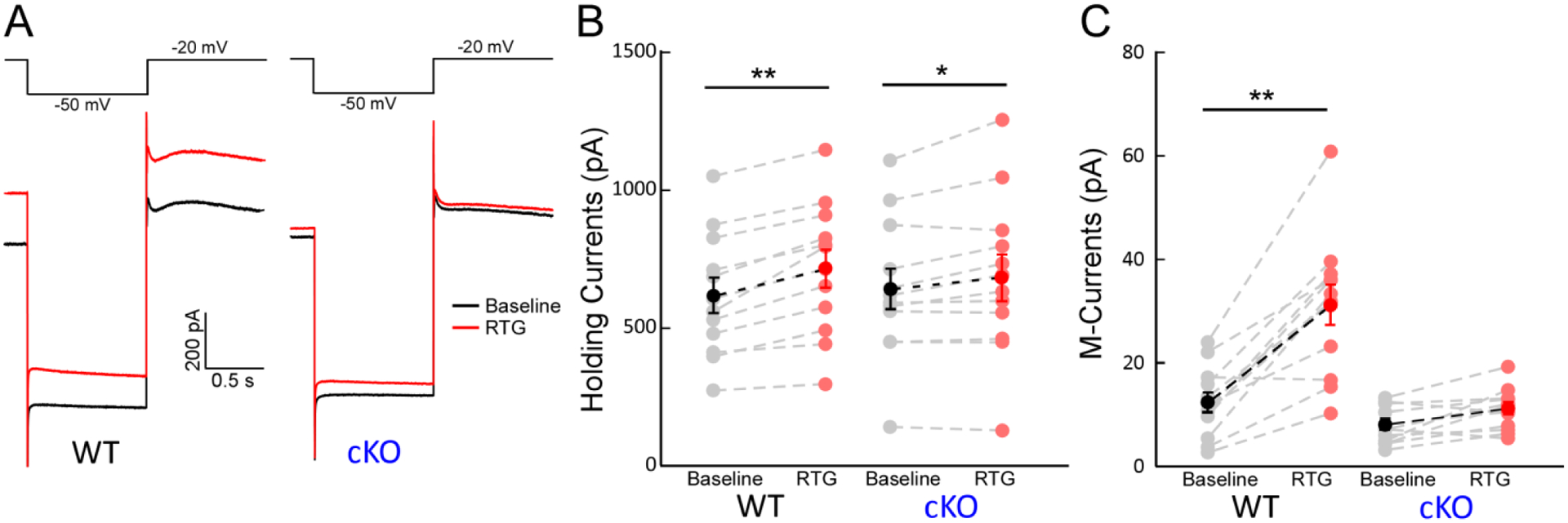
(A) Representative traces of M-currents (IM) in PV-INs from WT (left) and from cKO (right) before (black) and after (red) 10 μM RTG application. (B) RTG significantly increased the holding currents (Ihold) at −20 mV in PV-INs from WT (left, n = 12, Δ: 99.8 pA, **p < 0.01) and cKO mice (right, n = 12, Δ: 42.4 pA, *p < 0.05), but RTG had less effects on Ihold from cKO mice (interaction: F(1,1) = 6.9, p < 0.05 with two-way ANOVA). (C) RTG significantly increased the IM amplitude in PV-INs from WT mice, but not in PV-INs from cKO mice (WT, n=12, Δ: 18.7 pA, t=8.3, **p < 0.01; cKO, n=12; Δ: 3.14 pA, p > 0.05; interaction: F (1,1) = 24.1, p < 0.01 with two-way ANOVA).
