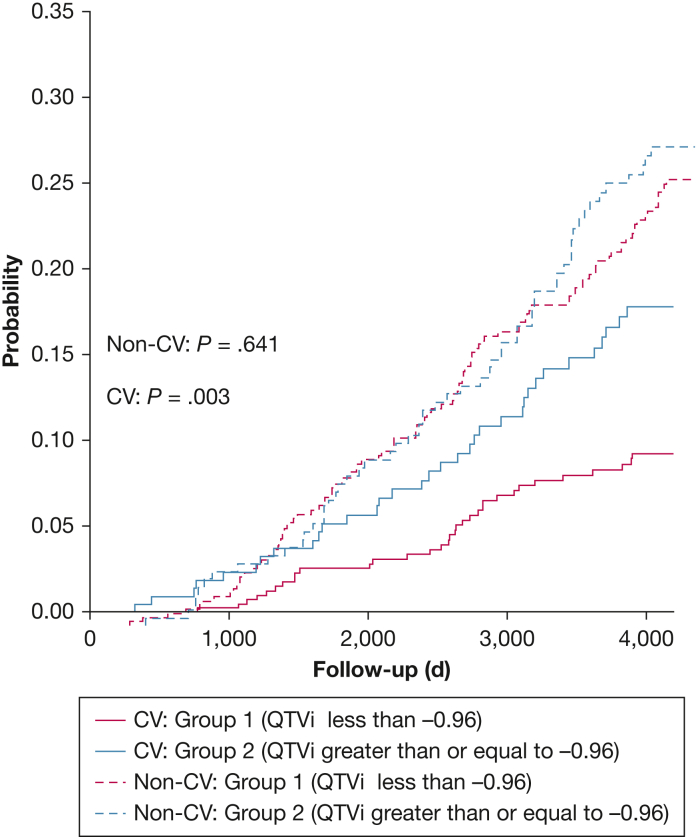
Figure 3.
The exposure-response relationship of arousal-related QTVi and CV mortality adjusted for age, history of stroke, myocardial infarction/coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, congestive heart failure, diabetes, hypertension, COPD, asthma, mean heart rate, mean respiratory rate, Physical Activity Scale for Elderly, systolic and diastolic blood pressures, time of sleep spent below 90% oxygen saturation, BMI, apnea-hypopnea index, arousal index, average corrected QT, arousal burden, and drink and smoking habit. CV = cardiovascular; QTVi = QT variability index.